
园艺学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (1): 257-274.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0996
石凤岩1, 魏美君2, 王秀雪1, 张曦1, 邹春蕾1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-04-01
修回日期:2025-11-25
出版日期:2026-01-25
发布日期:2026-01-26
通讯作者:
基金资助:
SHI Fengyan1, WEI Meijun2, WANG Xiuxue1, ZHANG Xi1, ZOU Chunlei1,*( )
)
Received:2025-04-01
Revised:2025-11-25
Published:2026-01-25
Online:2026-01-26
摘要:
辣椒疫病是由辣椒疫霉菌侵染引起的一种极具破坏性的土传病害,严重制约辣椒生产。目前辣椒抗疫病的分子机制尚不清楚,抗性基因的挖掘和功能分析是抗病育种的基础和前提。通过前期筛选,获得了对辣椒疫霉菌1、2和3号生理小种均表现免疫性的辣椒高代自交系ZCM334,该品系在接菌后,所有植株没有任何感病症状。在接菌后不同时间点(0、12、24和48 h)采集ZCM334和感病材料Early Calwonder的根部样本,并进行转录组测序和加权基因共表达网络分析(weighted gene co-expression network analysis,WGCNA)。共鉴定到17个共表达模块,其中4个与ZCM334抗疫病性呈显著正相关。功能富集分析结果显示,上述4个模块中的基因主要富集在植物激素信号转导、糖酵解、葡萄糖生成以及脂肪酸降解等代谢通路。对这4个模块作相关性分析,预测出12个可能与辣椒抗疫病相关的核心基因,其中包括6个已知功能基因(CA06g02420、CA06g08970、CA01g15560、CA09g14900、CA09g14910和CA09g15310)和6个新基因(novel.5608、novel.2732、novel.3300、novel.752、novel.2181和novel.12038),并构建了基因调控网络。qRT-PCR分析发现,这12个核心基因在ZCM334中显著高表达,且在接菌后24或48 h表达量最高。
石凤岩, 魏美君, 王秀雪, 张曦, 邹春蕾. 基于WGCNA的辣椒抗疫病关键基因的挖掘[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(1): 257-274.
SHI Fengyan, WEI Meijun, WANG Xiuxue, ZHANG Xi, ZOU Chunlei. Discovery of Key Genes for Pepper Resistance to Phytophthora Blight Based on WGCNA[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2026, 53(1): 257-274.
| 差异表达基因 DEGs ID | 正向引物(5′-3′)Forward primer | 反向引物(5′-3′)Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| novel.12038 | TGATCCAACTTTACCGATAACGAA | GTTGTCCAGACTCCAGAAGATGTT |
| CA06g02420 | GGAGCACTTATCAGGGAGGTATC | ACATCAAAAATACGTGCCCATAG |
| novel.2732 | CCAAACTCTTTCCTCAAAATCCA | GTGGCAAAGAAATAATAGACTCACATA |
| novel.3300 | AAGGCTCCGTTTTCTCTGACC | TTTGGAATAGGACTTGATGCGA |
| novel.5608 | TGAAAATGTATTGGCGTGCTG | ATGTAGTTGGCAAGTCGGGTAA |
| CA01g15560 | GGAGACAAGTCCCAGGGTGAG | ATCCCAGTCGGAAAATCATAGTT |
| novel.752 | CTTAGTCCCTTTTTGTTTGCGT | CTGCTCACCCTGAACCCTTTAG |
| CA06g08970 | GGTAGTTGACTTTCCTTCGGTAGC | CCAAATGACAAGAATACCCAAGG |
| novel.2181 | TCGTTTATGTGTTCTTGATTTTGC | TGAAACCAGCAGGAGGATTGA |
| CA09g14910 | GTGTGAGTTTGGCTTCAATGGA | TGGATTCAGATAAGTTCTTGCCC |
| CA09g14900 | ATCATCCTATTGTTTGGAGAGACC | AATAACCTTGTTGCCGAAGTAATC |
| CA09g15310 | CTGCCATTCCTACTTATGCTTGTG | GTTCTGCCTTGCCCTTTTCA |
| Actin | GACGTGACCTAACTGATAACCTGAT | CTCTCAGCACCAATGGTAATAACTT |
表1 用于验证辣椒抗疫病核心基因的qRT-PCR引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences for qRT-PCR validation of hub genes involved in pepper resistance to phytophthora blight
| 差异表达基因 DEGs ID | 正向引物(5′-3′)Forward primer | 反向引物(5′-3′)Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| novel.12038 | TGATCCAACTTTACCGATAACGAA | GTTGTCCAGACTCCAGAAGATGTT |
| CA06g02420 | GGAGCACTTATCAGGGAGGTATC | ACATCAAAAATACGTGCCCATAG |
| novel.2732 | CCAAACTCTTTCCTCAAAATCCA | GTGGCAAAGAAATAATAGACTCACATA |
| novel.3300 | AAGGCTCCGTTTTCTCTGACC | TTTGGAATAGGACTTGATGCGA |
| novel.5608 | TGAAAATGTATTGGCGTGCTG | ATGTAGTTGGCAAGTCGGGTAA |
| CA01g15560 | GGAGACAAGTCCCAGGGTGAG | ATCCCAGTCGGAAAATCATAGTT |
| novel.752 | CTTAGTCCCTTTTTGTTTGCGT | CTGCTCACCCTGAACCCTTTAG |
| CA06g08970 | GGTAGTTGACTTTCCTTCGGTAGC | CCAAATGACAAGAATACCCAAGG |
| novel.2181 | TCGTTTATGTGTTCTTGATTTTGC | TGAAACCAGCAGGAGGATTGA |
| CA09g14910 | GTGTGAGTTTGGCTTCAATGGA | TGGATTCAGATAAGTTCTTGCCC |
| CA09g14900 | ATCATCCTATTGTTTGGAGAGACC | AATAACCTTGTTGCCGAAGTAATC |
| CA09g15310 | CTGCCATTCCTACTTATGCTTGTG | GTTCTGCCTTGCCCTTTTCA |
| Actin | GACGTGACCTAACTGATAACCTGAT | CTCTCAGCACCAATGGTAATAACTT |

图1 辣椒材料ZCM334和Early Calwonder接种辣椒疫霉菌后的表型
Fig. 1 Comparison of disease-resistance phenotypes between pepper lines ZCM334 and Early Calwonder after inoculation with Phytophthora capsica

图2 接种辣椒疫霉后不同时间点后辣椒材料ZCM334和Early Calwonder样本的差异表达基因聚类热图
Fig. 2 Hierarchical clustering heatmap of differentially expressed genes in pepper lines ZCM334 and Early Calwonder at different time points after Phytophthora capsici inoculation

图3 辣椒根部转录组的加权基因共表达网络分析 A:软阈值的确定;B:基因聚类树和模块划分;C:基因共表达网络模块与不同样本的关联热图
Fig. 3 Weighted gene co-expression network analysis of the pepper root transcriptome A:Determination of soft threshold;B:Gene clustering tree and module partitioning;C:Correlation heatmap between gene co expression network modules and different samples

图4 与辣椒材料ZCM334抗疫病性正相关的核心模块基因的表达趋势
Fig. 4 Expression trends of core module genes positively associated with the resistance to Phytophthora capsici in pepper line ZCM334
| 基因 Gene ID | 模块 Model | 染色体 Chromosome | 基因功能描述 Gene description |
|---|---|---|---|
| CA08g08840 | 黄色Yellow | 8 | 转录延伸因子SPT5同源物 Transcription elongation factor SPT5 homolog |
| novel.7197 | 黄色Yellow | 7 | RNA介导的DNA聚合酶同源物 RNA-directed DNA polymerase homolog |
| novel.5036 | 黄色Yellow | 5 | 植物细胞内Ras相关的LRR蛋白 Plant intracellular Ras-group-related LRR protein |
| novel.6147 | 黄色Yellow | 6 | 细胞分化蛋白 RCD1 Cell differentiation protein RCD1 |
| novel.12038 | 黄色Yellow | 12 | 环核苷酸门控离子通道蛋白(CNGC) Cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel protein(CNGC) |
| novel.11518 | 黄色Yellow | 12 | 微管蛋白α-3链 Tubulin alpha-3 chain |
| novel.2994 | 黄色Yellow | 3 | 未知功能蛋白 Unknown protein |
| novel.5893 | 黄色Yellow | 6 | 线粒体腺嘌呤核苷酸转运蛋白ADNT1 Mitochondrial adenine nucleotide transporter ADNT1 |
| novel.1012 | 黄色Yellow | 1 | 未知功能蛋白 Unknown protein |
| novel.1435 | 黄色Yellow | 2 | 未鉴定的线粒体蛋白 Uncharacterized mitochondrial protein |
| CA06g02420 | 粉色Pink | 6 | 晚疫病抗性蛋白 Late blight resistance protein |
| novel.10180 | 粉色Pink | 10 | 细胞分裂素核苷5'-单磷酸磷酸核糖水解酶 Cytokinin riboside 5'-monophosphate phosphoribohydrolase |
| novel.2732 | 粉色Pink | 3 | F-box蛋白CPR30 Box protein CPR30 |
| novel.5609 | 粉色Pink | 6 | 未知功能蛋白 Unknown protein |
| novel.3300 | 粉色Pink | 3 | 细胞色素P450 Cytochrome P450 |
| CA09g02700 | 粉色Pink | 9 | 聚泛素 Polyubiquitin |
| novel.5608 | 粉色Pink | 6 | 晚疫病抗性蛋白 Late blight resistance protein |
| novel.5677 | 粉色Pink | 6 | 未知功能蛋白 Unknown protein |
| novel.6307 | 粉色Pink | 6 | 未知功能蛋白 Unknown protein |
| novel.9637 | 粉色Pink | 10 | RNA介导的DNA聚合酶同源物 RNA-directed DNA polymerase homolog |
| CA01g15560 | 洋红色Magenta | 1 | DEAD-box ATP依赖性RNA解旋酶 DEAD-box ATP-dependent RNA helicase |
| novel.646 | 洋红色Magenta | 1 | RNA导向的DNA聚合酶同源物 RNA-directed DNA polymerase homolog |
| CA12g10000 | 洋红色Magenta | 12 | 未知功能蛋白 Unknown protein |
| novel.752 | 洋红色Magenta | 1 | E4泛素连接酶 E4 ubiquitin ligase |
| CA11g05420 | 洋红色Magenta | 11 | α-淀粉酶3 α-amylase 3 |
| CA06g21380 | 洋红色Magenta | 6 | 胚胎发育晚期丰富蛋白 Late embryogenesis abundant protein |
| CA06g08970 | 洋红色Magenta | 6 | 高亲和力硝酸盐转运蛋白 High affinity nitrate transporter |
| CA08g08430 | 洋红色Magenta | 8 | 剪接因子SF3a60同源物 Splicing factor SF3a60 homolog |
| CA05g20820 | 洋红色Magenta | 5 | N6腺苷甲基转移酶亚基METTL14 N6-adenosine-methyltransferase subunit METTL14 |
| novel.2181 | 洋红色Magenta | 2 | 泛素结合酶 Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme |
| CA09g14910 | 棕褐色Tan | 9 | 早期结节样蛋白(ENODL) Early nodulin-like proteins(ENODL) |
| CA07g12450 | 棕褐色Tan | 7 | 未知功能蛋白 Unknown protein |
| novel.3819 | 棕褐色Tan | 4 | 蛋白酶抑制剂 Proteinase inhibitor |
| CA06g13600 | 棕褐色Tan | 6 | 非活性聚合物 Inactive poly |
| CA09g14900 | 棕褐色Tan | 9 | 萜烯合成酶 Terpene synthase |
| CA03g37000 | 棕褐色Tan | 3 | 丙氨酸氨基转移酶 Alanine aminotransferase |
| novel.3991 | 棕褐色Tan | 4 | 未知功能蛋白 Unknown protein |
| CA02g14150 | 棕褐色Tan | 2 | EP1样糖蛋白 EP1-like glycoprotein |
| CA12g11100 | 棕褐色Tan | 12 | 甾醇3-β-葡萄糖基转移酶 Sterol 3-β-glucosyltransferase |
| CA09g15310 | 棕褐色Tan | 9 | 早期结节样蛋白(ENODL) Early nodulin-like proteins(ENODL) |
表2 基于WGCNA筛选的辣椒抗疫病候选基因及其功能注释
Table 2 Candidate genes for pepper resistance to Phytophthora capsici screened by WGCNA and their functional annotation
| 基因 Gene ID | 模块 Model | 染色体 Chromosome | 基因功能描述 Gene description |
|---|---|---|---|
| CA08g08840 | 黄色Yellow | 8 | 转录延伸因子SPT5同源物 Transcription elongation factor SPT5 homolog |
| novel.7197 | 黄色Yellow | 7 | RNA介导的DNA聚合酶同源物 RNA-directed DNA polymerase homolog |
| novel.5036 | 黄色Yellow | 5 | 植物细胞内Ras相关的LRR蛋白 Plant intracellular Ras-group-related LRR protein |
| novel.6147 | 黄色Yellow | 6 | 细胞分化蛋白 RCD1 Cell differentiation protein RCD1 |
| novel.12038 | 黄色Yellow | 12 | 环核苷酸门控离子通道蛋白(CNGC) Cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel protein(CNGC) |
| novel.11518 | 黄色Yellow | 12 | 微管蛋白α-3链 Tubulin alpha-3 chain |
| novel.2994 | 黄色Yellow | 3 | 未知功能蛋白 Unknown protein |
| novel.5893 | 黄色Yellow | 6 | 线粒体腺嘌呤核苷酸转运蛋白ADNT1 Mitochondrial adenine nucleotide transporter ADNT1 |
| novel.1012 | 黄色Yellow | 1 | 未知功能蛋白 Unknown protein |
| novel.1435 | 黄色Yellow | 2 | 未鉴定的线粒体蛋白 Uncharacterized mitochondrial protein |
| CA06g02420 | 粉色Pink | 6 | 晚疫病抗性蛋白 Late blight resistance protein |
| novel.10180 | 粉色Pink | 10 | 细胞分裂素核苷5'-单磷酸磷酸核糖水解酶 Cytokinin riboside 5'-monophosphate phosphoribohydrolase |
| novel.2732 | 粉色Pink | 3 | F-box蛋白CPR30 Box protein CPR30 |
| novel.5609 | 粉色Pink | 6 | 未知功能蛋白 Unknown protein |
| novel.3300 | 粉色Pink | 3 | 细胞色素P450 Cytochrome P450 |
| CA09g02700 | 粉色Pink | 9 | 聚泛素 Polyubiquitin |
| novel.5608 | 粉色Pink | 6 | 晚疫病抗性蛋白 Late blight resistance protein |
| novel.5677 | 粉色Pink | 6 | 未知功能蛋白 Unknown protein |
| novel.6307 | 粉色Pink | 6 | 未知功能蛋白 Unknown protein |
| novel.9637 | 粉色Pink | 10 | RNA介导的DNA聚合酶同源物 RNA-directed DNA polymerase homolog |
| CA01g15560 | 洋红色Magenta | 1 | DEAD-box ATP依赖性RNA解旋酶 DEAD-box ATP-dependent RNA helicase |
| novel.646 | 洋红色Magenta | 1 | RNA导向的DNA聚合酶同源物 RNA-directed DNA polymerase homolog |
| CA12g10000 | 洋红色Magenta | 12 | 未知功能蛋白 Unknown protein |
| novel.752 | 洋红色Magenta | 1 | E4泛素连接酶 E4 ubiquitin ligase |
| CA11g05420 | 洋红色Magenta | 11 | α-淀粉酶3 α-amylase 3 |
| CA06g21380 | 洋红色Magenta | 6 | 胚胎发育晚期丰富蛋白 Late embryogenesis abundant protein |
| CA06g08970 | 洋红色Magenta | 6 | 高亲和力硝酸盐转运蛋白 High affinity nitrate transporter |
| CA08g08430 | 洋红色Magenta | 8 | 剪接因子SF3a60同源物 Splicing factor SF3a60 homolog |
| CA05g20820 | 洋红色Magenta | 5 | N6腺苷甲基转移酶亚基METTL14 N6-adenosine-methyltransferase subunit METTL14 |
| novel.2181 | 洋红色Magenta | 2 | 泛素结合酶 Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme |
| CA09g14910 | 棕褐色Tan | 9 | 早期结节样蛋白(ENODL) Early nodulin-like proteins(ENODL) |
| CA07g12450 | 棕褐色Tan | 7 | 未知功能蛋白 Unknown protein |
| novel.3819 | 棕褐色Tan | 4 | 蛋白酶抑制剂 Proteinase inhibitor |
| CA06g13600 | 棕褐色Tan | 6 | 非活性聚合物 Inactive poly |
| CA09g14900 | 棕褐色Tan | 9 | 萜烯合成酶 Terpene synthase |
| CA03g37000 | 棕褐色Tan | 3 | 丙氨酸氨基转移酶 Alanine aminotransferase |
| novel.3991 | 棕褐色Tan | 4 | 未知功能蛋白 Unknown protein |
| CA02g14150 | 棕褐色Tan | 2 | EP1样糖蛋白 EP1-like glycoprotein |
| CA12g11100 | 棕褐色Tan | 12 | 甾醇3-β-葡萄糖基转移酶 Sterol 3-β-glucosyltransferase |
| CA09g15310 | 棕褐色Tan | 9 | 早期结节样蛋白(ENODL) Early nodulin-like proteins(ENODL) |
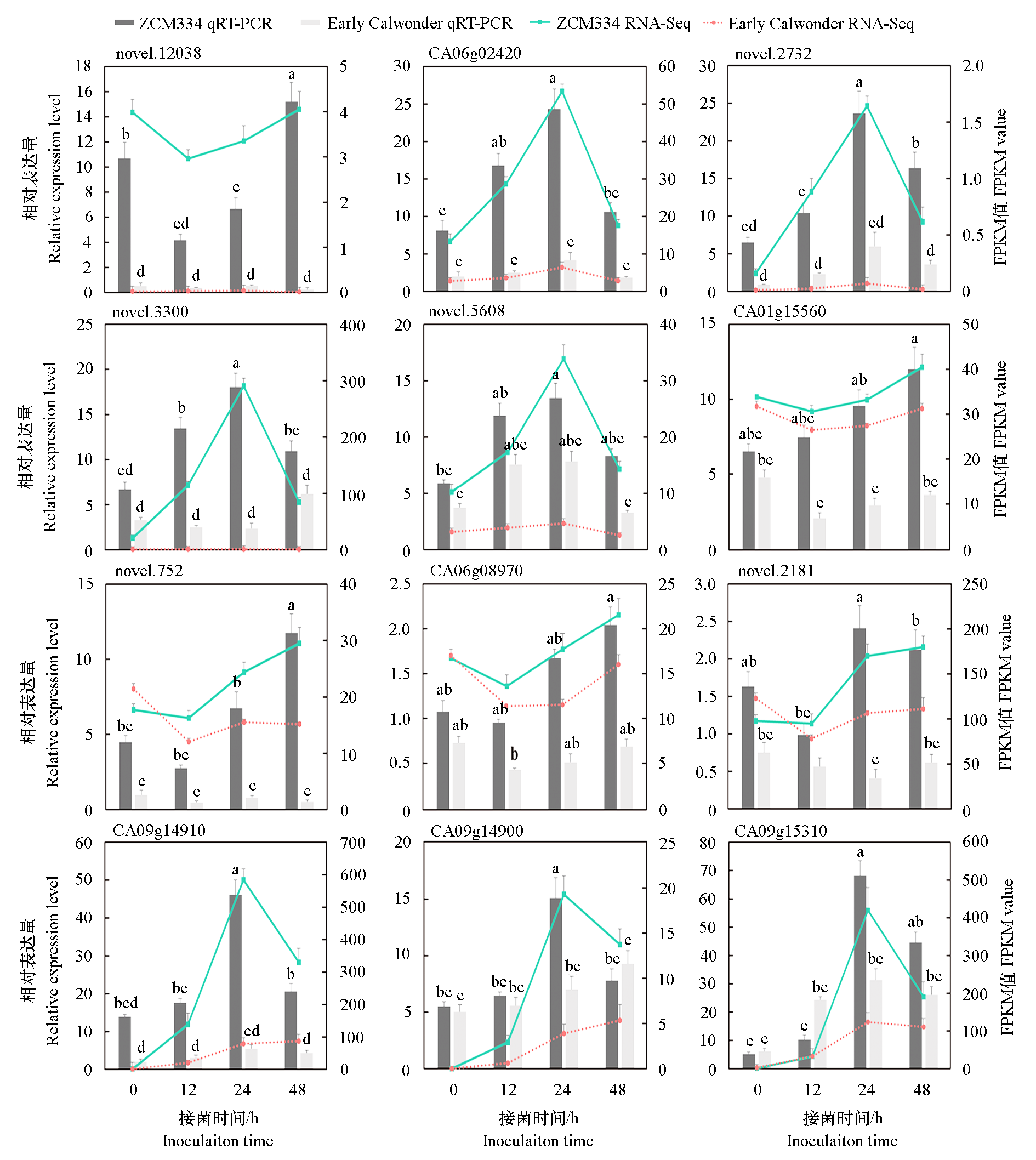
图8 辣椒抗疫病核心基因的qRT-PCR表达验证 不同小写字母表示不同处理间显著差异(P < 0.05)
Fig. 8 qRT-PCR based expression validation of hub genes involved in pepper resistance to phytophthora blight Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatmnet(P < 0.05)
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60608-3 pmid: 38969681 |
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05636-x pmid: 39396978 |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2009.60.issue-5 URL |
| [11] |
doi: 10.1094/PDIS-02-12-0211-FE pmid: 30727465 |
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2022.01.013 |
|
郭永春, 王鹏杰, 金珊, 侯炳豪, 王淑燕, 赵峰, 叶乃兴. 2022. 基于WGCNA鉴定茶树响应草甘膦相关的基因共表达模块. 中国农业科学, 55 (1):152-166.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2022.01.013 |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.119057 URL |
| [17] |
doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02711-x pmid: 33121441 |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2011.00754.x pmid: 22013895 |
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.1038/35015701 |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03387-7 |
| [27] |
|
|
马娟, 曹言勇, 王利锋, 李晶晶, 王浩, 范艳萍, 李会勇. 2020. 利用WGCNA鉴定玉米株高和穗位高基因共表达模块. 作物学报,46:385-394.
|
|
| [28] |
doi: 10.1007/s11032-013-9875-3 URL |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.117093 URL |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1111/pbi.v22.5 URL |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1094/PDIS.1998.82.11.1283A pmid: 30845427 |
| [32] |
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2020.94130 |
|
秦天元, 孙超, 毕真真, 梁文君, 李鹏程, 张俊莲, 白江平. 2020. 基于WGCNA的马铃薯根系抗旱相关共表达模块鉴定和核心基因发掘. 作物学报, 46 (7):1033-1051.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2020.94130 |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0350 |
|
石凤岩, 王治丹, 张曦, 王秀雪, 邹春蕾. 2024. 辣椒疫病抗性机制研究进展. 园艺学报, 51 (7):1665-1682.
|
|
| [36] |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37553-z |
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
doi: 10.3390/ijms241210047 URL |
| [41] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0769 |
|
王炫榛, 陈敏氡, 刘建汀, 曾美娟, 叶新如, 李永平, 温庆放, 朱海生. 2023. 普通丝瓜幼苗响应低温弱光核心基因共表达网络的WGCNA 鉴定. 园艺学报, 50 (12):2601-2618.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0769 |
|
| [42] |
doi: 10.3390/ijms231810770 URL |
| [43] |
|
|
谢丙炎, 朱国仁, 吴新平, 顾宝根, 刘乃炽. 2000. 辣椒疫霉产毒缺陷与抗药性突变体筛选及其遗传特性. 植物保护学报,(3):243-248.
|
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0626 |
|
袁娟伟, 贾利, 王涵, 严从生, 张其安, 俞飞飞, 甘德芳, 江海坤. 2025. 辣椒种质资源疫病抗性鉴定及抗病基因挖掘. 园艺学报, 52 (4):857-871.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0626 |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
doi: 10.1007/s11032-023-01367-3 |
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
|
周雨青, 杨永飞, 葛常伟, 沈倩, 张思平, 刘绍东, 马慧娟, 陈静, 刘瑞华, 李士丛. 2022. 基于WGCNA的棉花子叶抗冷相关共表达模块鉴定. 中国农业科技导报, 24 (4):11.
|
| [1] | 邹学校, 李国琛, 庹炼, 杨莎, 朱凡, 徐昊, 胡博文, 熊程, 戴雄泽, 远方. 南疆辣椒产业高质量发展优势与对策[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(1): 303-312. |
| [2] | 凃祥敏, 吴迪, 刘崇政, 赖卫, 何建文, 杨红. 辣椒新品种‘黔辣9号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 139-140. |
| [3] | 陈学军, 方荣, 周坤华, 袁欣捷, 雷刚, 黄月琴. 辣椒新品种‘棕辣1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 141-142. |
| [4] | 白立伟, 朱文超, 胡明文, 廖芳芳. 辣椒新品种‘辣研511’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 143-144. |
| [5] | 黄贞, 郑岩松, 李光光. 辣椒新品种‘辣优22号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 145-146. |
| [6] | 何烈干, 聂武学, 邹芬, 王春庆, 余君辉, 黄小妹, 黄水林, 马辉刚. 辣椒新品种‘赣辣1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 147-148. |
| [7] | 何烈干, 聂武学, 王春庆, 邹芬, 余君辉, 黄小妹, 黄水林, 马辉刚. 辣椒新品种‘赣辣娇龙’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 149-150. |
| [8] | 尹延旭, 李宁, 高升华, 徐凯, 王小迪, 詹晓慧, 袁伟玲, 陈卫芳, 任志勇, 王飞, 姚明华. 加工辣椒新品种‘鄂干椒105’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 151-152. |
| [9] | 李秉衡, 周书栋, 吴波, 杨光彬, 杨博智, 李雪峰, 童龙. 高品质鲜食辣椒新品种‘兴蔬211’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 153-154. |
| [10] | 刘子记, 秦于玲, 刘维侠, 朱丹, 殷晓敏, 曹振木. 工业辣椒新品种‘热辣8号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 155-156. |
| [11] | 刘术均. 中晚熟辣椒新品种‘姆利特’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 115-116. |
| [12] | 朱世银, 涂国静, 李 翔, 蔡荣靖, 刘贤梅, 王 灿, 杨 菊, 肖德琴, 阮俊光, 马梅见, 刘 莹, 叶国琼, 胡德波. 辣椒新品种‘昭椒3号’和‘昭椒4号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 117-118. |
| [13] | 邹 芬, 聂武学, 项 青, 何烈干, 王春庆, 余君辉, 黄小妹, 黄水林, 马辉刚. 辣椒新品种‘月红461’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 119-120. |
| [14] | 卢景琪, 刘 峰, 邹学校. 辣椒新品种‘润疆红17号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 121-122. |
| [15] | 王广华, 李 磊, 刘 玲. 加工型辣椒新品种‘红宝塔’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 123-124. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司