
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (10): 2737-2747.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0867
孙美华1,*, 孙慧贤1,*, 赵晏俪1, 李婧1, 田林林1, 苗妍秀1, 白龙强1, 侯雷平1, 张毅1, 李天来2,**( )
)
收稿日期:2024-10-31
修回日期:2025-06-01
出版日期:2025-10-25
发布日期:2025-10-28
通讯作者:
作者简介:*共同第一作者
基金资助:
SUN Meihua1, SUN Huixian1, ZHAO Yanli1, LI Jing1, TIAN Linlin1, MIAO Yanxiu1, BAI Longqiang1, HOU Leiping1, ZHANG Yi1, LI Tianlai2,**( )
)
Received:2024-10-31
Revised:2025-06-01
Published:2025-10-25
Online:2025-10-28
摘要:
采用不同氮浓度的营养液处理番茄幼苗,分析其茎尖内营养物质含量、酶活性、内源激素含量及基因表达变化,以探究不同供氮水平调控番茄心室数量的作用机制。结果显示,提高氮营养水平,可促进番茄花芽分化,增加果实心室数量和幼苗茎尖内可溶性蛋白质、淀粉、蔗糖、可溶性糖的含量及POD、NR、PPO酶活性,与果实心室数量密切相关的是可溶性蛋白质、可溶性糖含量及POD、NR、PPO活性;提高氮营养水平还增加了幼苗茎尖细胞分裂素、赤霉素、茉莉酸含量。转录组筛选出与花芽分化密切相关的过氧化物酶基因PRX44-like、PRX3-like和PRX66,赤霉素合成基因GA2ox2,细胞分裂素合成基因TLOG1、CKX2。结合生理指标变化,推测提高苗期氮营养水平,可能通过调控PRX44-like和GA2ox2基因表达,增加POD酶活性和赤霉素含量,进而影响番茄果实心室数量。
孙美华, 孙慧贤, 赵晏俪, 李婧, 田林林, 苗妍秀, 白龙强, 侯雷平, 张毅, 李天来. 不同供氮水平对番茄果实心室数量的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(10): 2737-2747.
SUN Meihua, SUN Huixian, ZHAO Yanli, LI Jing, TIAN Linlin, MIAO Yanxiu, BAI Longqiang, HOU Leiping, ZHANG Yi, LI Tianlai. Effects of Different Nitrogen Concentration on the Locule Number in Tomato Fruit[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(10): 2737-2747.
| 氮水平N level | KNO3 | Ca(NO3)2 · 4H2O | NaH2PO4 · 4H2O | KH2PO4 | NH4NO3 | CaCl2 | MgSO4 | N | P2O5 | K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 标准Normal | 301 | 912 | 395.5 | -- | -- | -- | 400 | 150 | 180 | 140 |
| 多High | 301 | 912 | 395.5 | -- | 286 | -- | 400 | 250 | 180 | 140 |
| 少Low | 301 | 70 | 395.5 | -- | -- | 748 | 400 | 50 | 180 | 140 |
表1 不同处理营养液配方(大量元素部分)
Table 1 Nutrient solution formulations for different treatments(large elements) mg · L-1
| 氮水平N level | KNO3 | Ca(NO3)2 · 4H2O | NaH2PO4 · 4H2O | KH2PO4 | NH4NO3 | CaCl2 | MgSO4 | N | P2O5 | K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 标准Normal | 301 | 912 | 395.5 | -- | -- | -- | 400 | 150 | 180 | 140 |
| 多High | 301 | 912 | 395.5 | -- | 286 | -- | 400 | 250 | 180 | 140 |
| 少Low | 301 | 70 | 395.5 | -- | -- | 748 | 400 | 50 | 180 | 140 |
| 目的基因Target gene | 引物序列(5′-3′)Primer sequence | |
|---|---|---|
| GA2ox2 | F:ATTCGGGCTGCGGTTAATGA | R:TCAATCTCTGAGCATGGCGG |
| TLOG1 | F:AAGAGCAGTGTCTGGGATGC | R:AATGATGTGACGGGCAGAGG |
| CKX2 | F:CAAGAGGCCACGGTCATTCT | R:TGTCCACTGATGCCAGCATT |
| PRX44 | F:GGGCCTAGTATAACGGTGCC | R:TGGCGACCCACCATTAGAAC |
| PRX3 | F:ATGCACCATCTCTTGCTGCT | R:GCACATGACACAATCCCAGG |
| PRX66 | F:CTCGAAAAGGCTTGCCCAAC | R:CCAAGTGTGTGTCCACCAGA |
| ACTIN | F:GATCAGCGTATCCTTCAGAG | R:GGCATTGTAGCAGAGAAAAC |
表2 实时荧光定量试验所用引物
Table 2 Primers used in real-time fluorescence quantitative experiments
| 目的基因Target gene | 引物序列(5′-3′)Primer sequence | |
|---|---|---|
| GA2ox2 | F:ATTCGGGCTGCGGTTAATGA | R:TCAATCTCTGAGCATGGCGG |
| TLOG1 | F:AAGAGCAGTGTCTGGGATGC | R:AATGATGTGACGGGCAGAGG |
| CKX2 | F:CAAGAGGCCACGGTCATTCT | R:TGTCCACTGATGCCAGCATT |
| PRX44 | F:GGGCCTAGTATAACGGTGCC | R:TGGCGACCCACCATTAGAAC |
| PRX3 | F:ATGCACCATCTCTTGCTGCT | R:GCACATGACACAATCCCAGG |
| PRX66 | F:CTCGAAAAGGCTTGCCCAAC | R:CCAAGTGTGTGTCCACCAGA |
| ACTIN | F:GATCAGCGTATCCTTCAGAG | R:GGCATTGTAGCAGAGAAAAC |

图1 不同供氮水平对番茄花芽分化进程(A,B)、花大小(C,D)和花器官数量(E)的影响 Duncan’s检验,不同的小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P < 0.05)
Fig. 1 Effects of different nitrogen concentrations on tomato flowers bud differentiation process(A,B),flower size(C,D)and number of floral organs(E) Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference among treatments(P < 0.05)according to Duncan’s multiple range tests
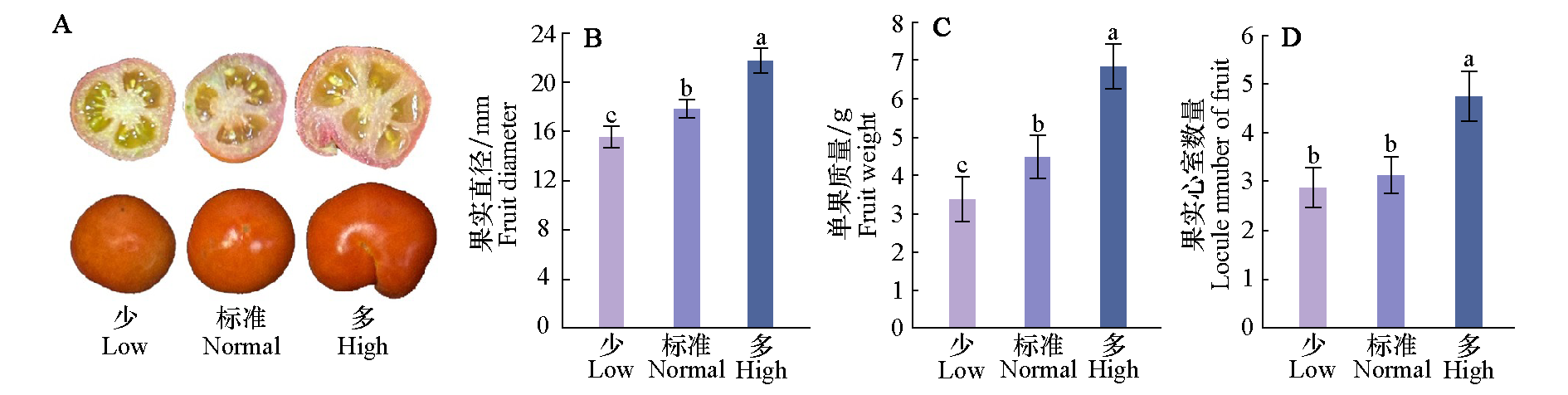
图2 不同供氮水平对番茄果实(A)、果实大小(B)、单果质量(C)和心室数量(D)的影响 Duncan’s检验,不同的小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P < 0.05)
Fig. 2 Effects of different nitrogen concentrations on tomato fruit(A),fruit size(B),fruit weight(C)and locule number(D) Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference among treatments(P < 0.05)according to Duncan’s multiple range tests
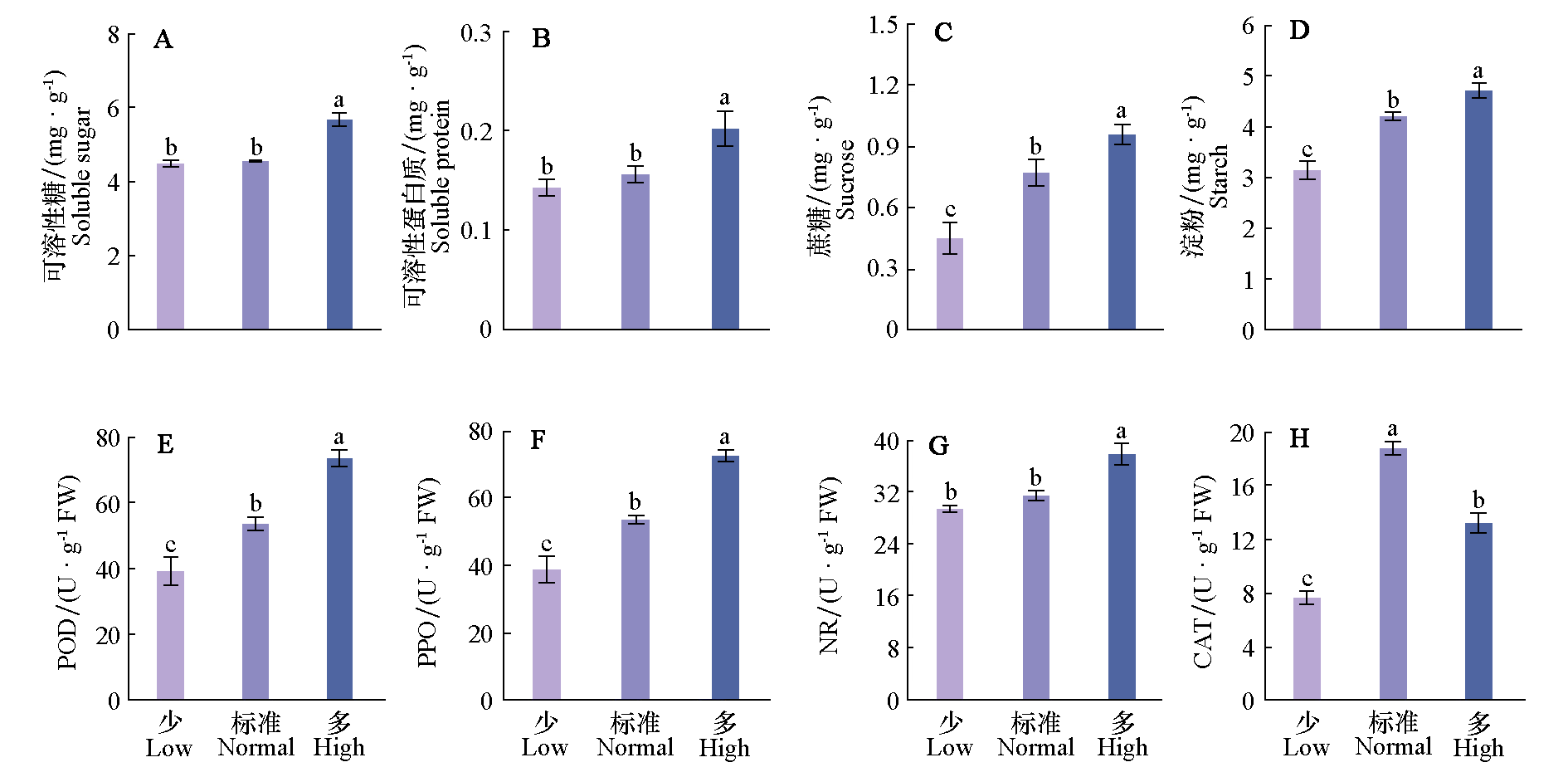
图3 不同供氮水平对番茄幼苗茎尖内营养物质含量和酶活性的影响 根据Duncan’s检验方法,不同的小写字母表示处理间差异显著性(P < 0.05)
Fig. 3 Effects of different nitrogen concentrations on nutrient content and enzyme activity in stem apex of tomato seedlings Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference among treatments(P < 0.05)according to Duncan’s multiple range tests
| 性状 Trait | 可溶性蛋白 Soluble protein | 淀粉 Starch | 蔗糖 Sucrose | 可溶性糖 Solube sugar | POD | NR | CAT | PPO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 花直径Flower size | 0.964** | 0.014 | 0.821** | 0.969** | 0.929** | 0.963** | 0.152 | 0.929** |
| 果实直径Fruit size | 0.961** | 0.080 | 0.876** | 0.868** | 0.934** | 0.919** | 0.379 | 0.968** |
| 单果质量Single fruit weight | 0.942** | 0.129 | 0.910** | 0.880** | 0.960** | 0.913** | 0.445 | 0.986** |
| 心室数量Locule number | 0.845** | -0.277 | 0.642 | 0.812** | 0.770* | 0.939** | -0.040 | 0.785* |
表3 番茄幼苗茎尖内营养物质含量和酶活性与花和果实性状的相关性分析
Table 3 Correlation analysis of nutrient content and enzyme activity in stem apex of seedlings with flower and fruit traits
| 性状 Trait | 可溶性蛋白 Soluble protein | 淀粉 Starch | 蔗糖 Sucrose | 可溶性糖 Solube sugar | POD | NR | CAT | PPO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 花直径Flower size | 0.964** | 0.014 | 0.821** | 0.969** | 0.929** | 0.963** | 0.152 | 0.929** |
| 果实直径Fruit size | 0.961** | 0.080 | 0.876** | 0.868** | 0.934** | 0.919** | 0.379 | 0.968** |
| 单果质量Single fruit weight | 0.942** | 0.129 | 0.910** | 0.880** | 0.960** | 0.913** | 0.445 | 0.986** |
| 心室数量Locule number | 0.845** | -0.277 | 0.642 | 0.812** | 0.770* | 0.939** | -0.040 | 0.785* |
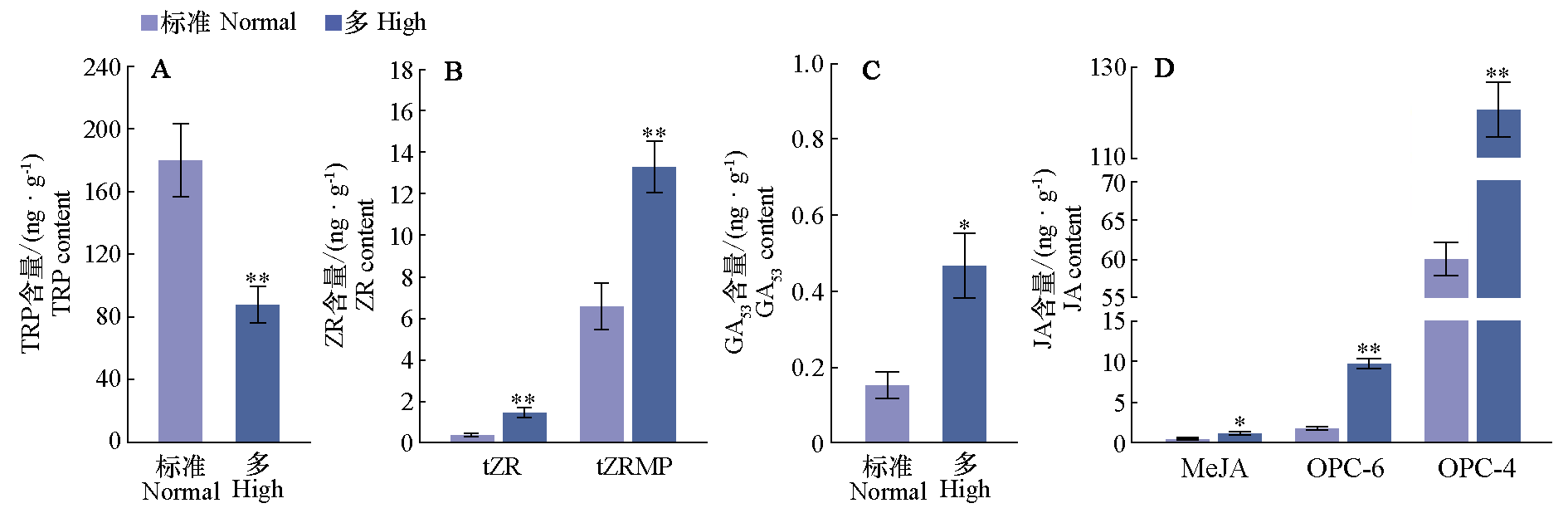
图4 多氮对番茄幼苗茎尖中激素含量的影响 独立样本t检验,* 表示在P < 0.05水平具有显著性,** 表示在P < 0.01水平具有显著性
Fig. 4 Effects of high nitrogen concentration on hormone content in stem apex of tomato seedlings * means significant at P < 0.05 level,** means significant at P < 0.01 level according to the Independent t-test
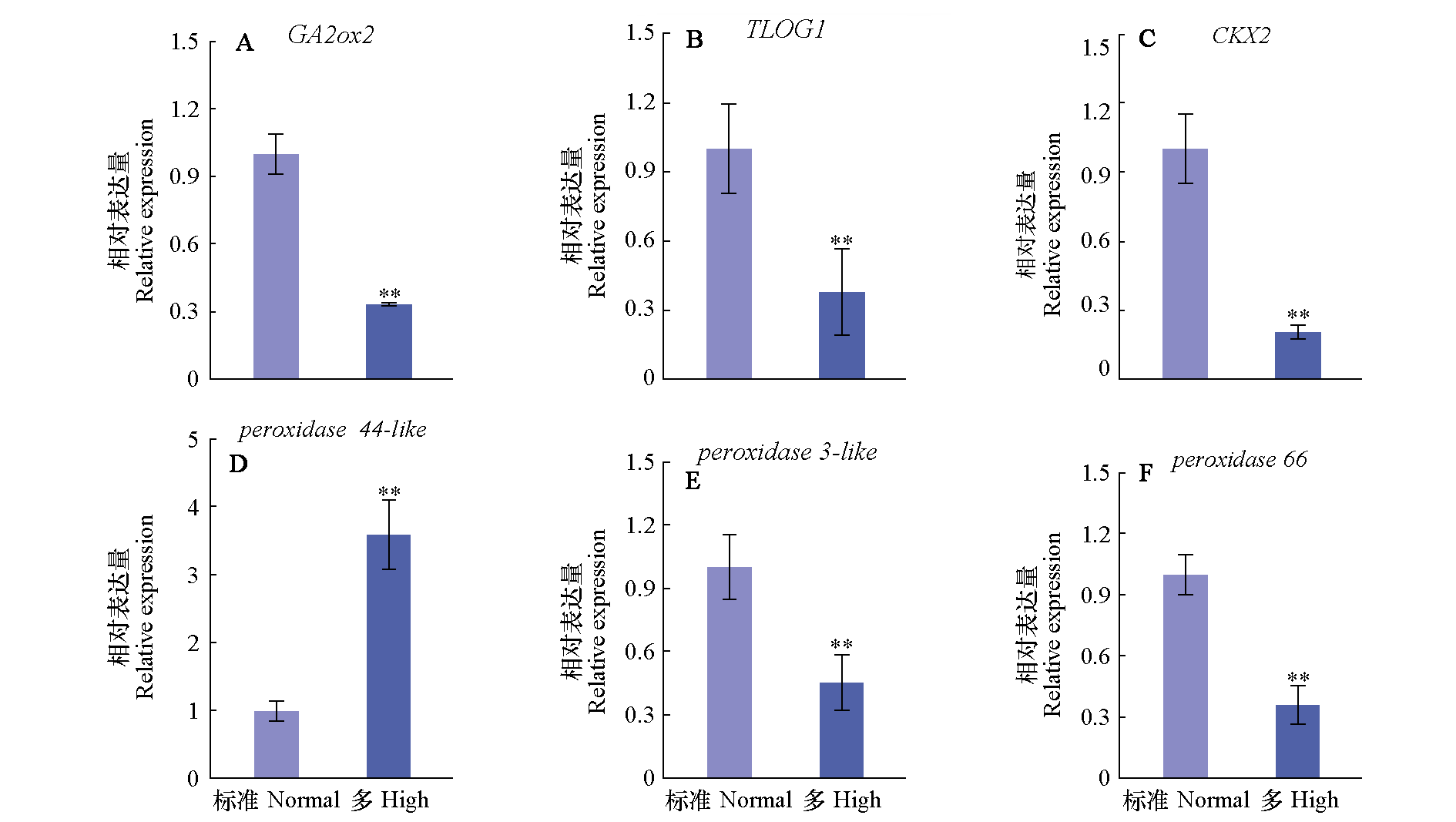
图5 多氮对番茄幼苗茎尖中基因表达的影响 * 表示在P < 0.05水平具有显著性,** 表示在P < 0.01水平具有显著性
Fig. 5 Effects of high nitrogen concentration on gene expression in stem apex of tomato seedlings * means significant at P < 0.05 level,** means significant at P < 0.01 level
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
|
陈先知. 2005. 苗期光、温、养分对“川番杂交一号”番茄畸形果发生的影响研究[硕士论文]. 成都: 四川农业大学.
|
|
| [3] |
|
|
陈先知, 李能芳, 朱剑桥, 朱隆静. 2006. 苗期夜温对番茄畸形果发生的影响. 四川农业大学学报, 24 (3):309-312.
|
|
| [4] |
doi: 10.1038/ng.144 pmid: 18469814 |
| [5] |
|
|
高俊凤. 2006. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京:高等教育出版社:210-217.
|
|
| [6] |
|
|
胡静, 饶桦静, 裴瑾, 唐小慧, 刘钰萍, 魏担, 耿福昌. 2018. 西红花花芽分化的形态发育及生理生化变化研究. 中药材, 41 (12):2748-2752.
|
|
| [7] |
|
|
黄洁衔, 李腾基, 黄紫钦, 逯有法, 张建霞. 2023. 墨兰花芽形态分化及生理特性研究. 北方园艺,(3):56-63.
|
|
| [8] |
|
|
孔德政, 靳丹丹, 孙丽娜, 管志涛, 毛瑞丽. 2008. 碗莲花芽分化过程中酶活性的变化. 河南农业科学,(4):97-99.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3268.2008.04.028 |
|
| [9] |
|
|
李会. 2018. lc位点通过SlWUS基因调控番茄子房心室形成的研究[博士论文]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学.
|
|
| [10] |
|
|
李天来, 房思强, 郭泳, 杨延杰, 藤少明. 1997. 植物生长调节剂对番茄畸形果发生的影响. 沈阳农业大学学报, 28 (3):30-34.
|
|
| [11] |
|
|
李天来, 须晖, 郭泳, 姜涛. 2000. 苗期不同灌水点对番茄畸形果发生的影响//中国园艺学会第四届青年学术讨论会论文集:358-361.
|
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
|
李艳冰. 2021. 苗期低夜温诱导番茄心室增多的赤霉素作用机制[博士论文]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学.
|
|
| [14] |
|
|
李悦, 李天来, 王丹. 2008. 番茄花芽分化期茎尖内源激素水平与果实心室数目的相关性研究. 中国农业科学,(9):2727-2733.
|
|
| [15] |
|
|
刘爽. 2012. 赤霉素与fasciated在调控番茄心室形成中的作用关系分析[博士论文]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学.
|
|
| [16] |
|
|
孟思达, 韩磊磊, 相恒佐, 朱美玉, 冯珍, 叶云珠, 孙美华, 李艳冰, 赵利萍, 谭昌华, 齐明芳, 李天来. 2024. 番茄心室数的调控机制研究进展. 园艺学报, 51 (7):1649-1664.
|
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.111.173997 pmid: 21673133 |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1038/nprot.2010.37 pmid: 20448544 |
| [19] |
|
|
乔双. 2014. 生长素与fasciated在调控番茄心室形成中的作用关系[硕士论文]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学.
|
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
|
王学奎, 黄见良. 2015. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社.
|
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
|
吴洁秋, 朱根发, 王凤兰, 杨凤玺. 2021. 竹叶兰花器官发育过程及生理特性研究. 热带作物学报, 42 (1):140-148.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2021.01.020 |
|
| [25] |
|
|
吴新亮. 2020. 细胞分裂素对番茄多心室畸形果的调控作用研究[硕士论文]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学.
|
|
| [26] |
|
|
吴志斌. 2022. 生长素缓解低夜温下番茄多心室畸形果发生的机制解析[硕士论文]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学.
|
|
| [27] |
doi: 10.1038/ng.3309 pmid: 26005869 |
| [28] |
|
|
须晖, 李天来, 郭泳, 杨丽娟. 1997. 苗期营养水平对番茄畸形果发生的影响. 中国蔬菜,(5):12-14.
|
|
| [29] |
|
|
须晖, 孙红梅, 郭泳, 杨丽娟, 李天来, 房思强. 1999. 番茄苗期营养及其幼苗茎尖物质含量与畸形果发生的关系//中国园艺学会成立70周年纪念优秀论文选编:476-480.
|
|
| [30] |
|
|
须晖, 李天来, 郭泳, 陈伟之, 杨丽娟, 鄂文伟. 2000. 番茄幼苗体内激素含量与畸形果发生的关系//中国园艺学会第四届青年学术讨论会论文集:360-364.
|
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
|
姚凯, 牛晓娟, 徐僡, 敖家林. 2019. 锶对菠菜幼苗生长、光合和抗氧化酶活性的影响. 核农学报, 33 (6):1225-1231.
doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2019.06.1225 |
| [1] | 宰文珊, 陈先知, 付存念, 苏世闻, 史建磊, 熊自立, 黄少勇. 口感番茄新品种‘瓯秀901’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 121-122. |
| [2] | 王荣青, 姚祝平, 程远, 叶青静, 阮美颖, 万红建, 李志邈, 刘晨旭, 周国治. 高品质耐贮运番茄新品种‘浙粉718’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 123-124. |
| [3] | 郑梦凡, 谢勇, 郑伟, 李光乾, 陈刚, 王煜双, 李聪, 张余洋. 优质番茄新品种‘民丰698’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 125-126. |
| [4] | 朱鹏宇, 谢勇, 郑伟, 李光乾, 陈刚, 王煜双, 李聪, 张余洋. 优质番茄新品种‘希唯美191’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 127-128. |
| [5] | 崔爱花, 朱模勇, 张扬栋, 伍琦, 刘帅, 胡启星, 黄纪刚, 刘家鑫, 刘为胜, 孙巨龙. 大果型番茄新品种‘奥丽亚’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 129-130. |
| [6] | 郑于莉, 刘燕, 潘子旺, 韩兰兰, 李凯, 刘丹, 曹阳, 芦鑫哲, 康永生. 多抗硬粉番茄新品种‘BY002’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 131-132. |
| [7] | 苏世闻, 付存念, 陈先知, 崔丽利, 史建磊, 黄少勇, 熊自立, 宰文珊. 樱桃番茄新品种‘瓯秀红樱5号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 133-134. |
| [8] | 付存念, 苏世闻, 陈先知, 崔丽利, 史建磊, 黄少勇, 熊自立, 宰文珊. 樱桃番茄新品种‘瓯秀橙樱1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 135-136. |
| [9] | 熊自立, 苏世闻, 史建磊, 张海利, 宰文珊, 崔丽利. 番茄砧木新品种‘瓯砧1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 137-138. |
| [10] | 范惠冬, 郑士金, 田 松, 郑建超. 番茄新品种‘吉粉7号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 109-110. |
| [11] | 张立微, 戴忠仁, 陈青奇, 雷 娜, 胡海江, 门万杰. 番茄新品种‘哈研中粉果1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 111-112. |
| [12] | 熊自立, 史建磊, 陈勇兵, 张海利, 苏世闻, 宰文珊, 叶曙光. 设施番茄新品种‘瓯秀202’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 113-114. |
| [13] | 王雅慧, 张雨晴, 张榕蓉, 刘佩卓, 梁毅, 周建华, 熊爱生. 胡萝卜番茄红素ε-环化酶基因DcLCYE启动子活性分析及互作因子筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(9): 2317-2328. |
| [14] | 陈舒婷, 吴幕绵, 李涛, 黎振兴, 麦培婷, 孙保娟, 郝彦伟, 宫超. 有效微生物群落对番茄产量及根际土壤细菌群落的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(9): 2477-2490. |
| [15] | 苏秀敏, 王佼, 韩文清, 李鹏, 王秋兰, 李万星. 山西长治番茄枯萎病病原鉴定及其拮抗菌鉴选[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(9): 2532-2544. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司