
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (5): 883-896.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0450
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Zumin1, XIAO Nuoya1, ZHANG Yanxia2, SHI Xiaomin1, GUO Shuaiqi1, GAO Hu1, WANG Zhenping1,*( )
)
Received:2020-11-20
Revised:2021-02-25
Online:2021-05-25
Published:2021-06-07
Contact:
WANG Zhenping
E-mail:wangzhp@163.com
CLC Number:
CHEN Zumin, XIAO Nuoya, ZHANG Yanxia, SHI Xiaomin, GUO Shuaiqi, GAO Hu, WANG Zhenping. Effects of Water Stress on the Volatile Compounds and Related Biosynthetic Genes Expression in‘Muscat Hamburg’Grape Berries[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(5): 883-896.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0450
| 处理 Treatment | 黎明前叶片水势(Ψb)/MPa Predawn leaf water potential |
|---|---|
| 对照 Control | -0.20 ~-0.40 |
| 轻度胁迫 Light water stress | -0.40 ~-0.60 |
| 重度胁迫 Severe water stress | ≤-0.60 |
Table 1 Reference standard of leaf water potential of different treatments
| 处理 Treatment | 黎明前叶片水势(Ψb)/MPa Predawn leaf water potential |
|---|---|
| 对照 Control | -0.20 ~-0.40 |
| 轻度胁迫 Light water stress | -0.40 ~-0.60 |
| 重度胁迫 Severe water stress | ≤-0.60 |
| 基因名称 Gene name | 基因登录号 Accession number | 引物序列(5′-3′) Sequence of primer |
|---|---|---|
| VvGPPS | AY351862.1 | F:AACTGCGGAAGTTTCAATGTTGGC;R:ATGGCGGATGTCAGACAATGAACC |
| VvRiLinNer | JQ062931.1 | F:AGTTGGAGAGGATACGCTGGAAGG;R:CTCACCGTGAGTGCTGGCTTTC |
| VvTPS | NM_001281134.1 | F:GTCGGGTCAAGTCTTAGCAAGCC;R:GTTACCTCGTCCTCGGGAGTGTAG |
| VvCCD1 | NM_001280915.1 | F:TGGCACTTTCGGAGGCTGATAAAC;R:GGGTCAACCTTTGGATGAGCAGTG |
| VvActin | EC969944 | F:CTTGCATCCCTCAGCACCTT;R:TCCTGTGGACAATGGATGGA |
Table 2 Primer sequences for real-time quantitative PCR
| 基因名称 Gene name | 基因登录号 Accession number | 引物序列(5′-3′) Sequence of primer |
|---|---|---|
| VvGPPS | AY351862.1 | F:AACTGCGGAAGTTTCAATGTTGGC;R:ATGGCGGATGTCAGACAATGAACC |
| VvRiLinNer | JQ062931.1 | F:AGTTGGAGAGGATACGCTGGAAGG;R:CTCACCGTGAGTGCTGGCTTTC |
| VvTPS | NM_001281134.1 | F:GTCGGGTCAAGTCTTAGCAAGCC;R:GTTACCTCGTCCTCGGGAGTGTAG |
| VvCCD1 | NM_001280915.1 | F:TGGCACTTTCGGAGGCTGATAAAC;R:GGGTCAACCTTTGGATGAGCAGTG |
| VvActin | EC969944 | F:CTTGCATCCCTCAGCACCTT;R:TCCTGTGGACAATGGATGGA |
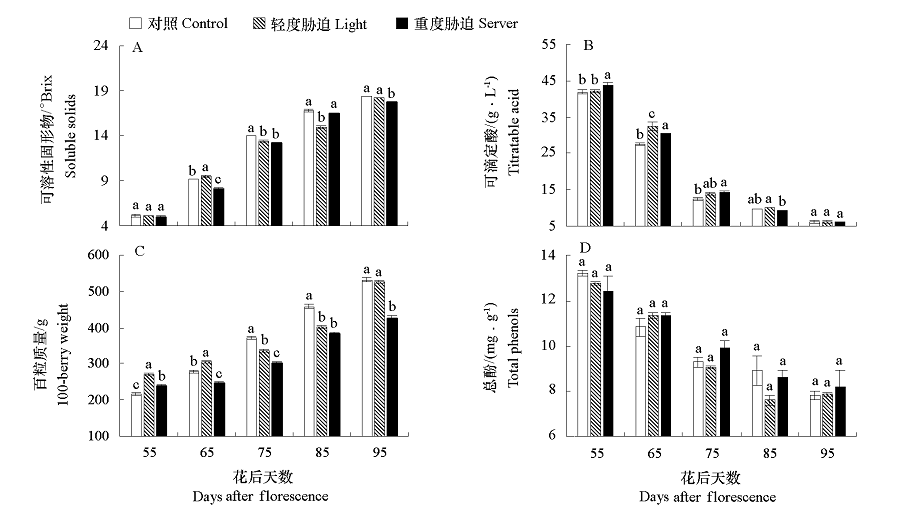
Fig. 2 Effect of berry quality of‘Muscat Hamburg’grape under different water stresses Different letters mean significant different at 0.05 level. The same below.
| 处理 Treatment | 酸类 Acid | 酯类 Ester | 酮类 Ketone | 醛类 Aldehyde | 醇类 Alcohol | 萜烯类 Terpene | 酚类 Phenolic | 其他类 Others | 总计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照Control | 8 | 1 | 8 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 1 | 2 | 41 |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 7 | 2 | 8 | 7 | 3 | 8 | 1 | 7 | 43 |
| 重度胁迫Severe | 5 | 1 | 6 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 33 |
Table 3 Number of species of water stress on volatile compounds of‘Muscat Hamburg’grape at mature stage
| 处理 Treatment | 酸类 Acid | 酯类 Ester | 酮类 Ketone | 醛类 Aldehyde | 醇类 Alcohol | 萜烯类 Terpene | 酚类 Phenolic | 其他类 Others | 总计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照Control | 8 | 1 | 8 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 1 | 2 | 41 |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 7 | 2 | 8 | 7 | 3 | 8 | 1 | 7 | 43 |
| 重度胁迫Severe | 5 | 1 | 6 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 33 |
| 处理 Treatment | 酸类 Acid | 酯类 Ester | 酮类 Ketone | 醛类 Aldehyde | 醇类 Alcohol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照 Control | 24.58 ± 4.39 b | 3.76 ± 2.13 b | 48.53 ± 11.09 a | 595.41 ± 69.00 b | 123.39 ± 19.82 b |
| 轻度胁迫 Light | 21.28 ± 9.10 b | 5.94 ± 3.63 a | 46.70 ± 17.36 a | 1 054.23 ± 215.11 a | 8.74 ± 1.04 c |
| 重度胁迫 Severe | 67.14 ± 16.98 a | 3.16 ± 1.93 b | 24.12 ± 10.60 b | 446.73 ± 45.51 c | 133.06 ± 30.63 a |
| 处理 Treatment | 萜烯类 Terpene | 酚类 Phenolic | 其他类 Others | 总计 Total | |
| 对照 Control | 400.48 ± 43.46 c | 3.18 ± 1.59 b | 13.78 ± 2.84 b | 1 213.11 ± 146.02 b | |
| 轻度胁迫 Light | 442.33 ± 43.07 b | 10.63 ± 4.60 a | 44.75 ± 7.93 a | 1 634.60 ± 277.05 a | |
| 重度胁迫 Severe | 497.98 ± 79.71 a | 2.59 ± 0.92 b | 19.07 ± 7.72 b | 1 193.85 ± 187.22 b |
Table 4 Effect of water stress on volatile compounds content of‘Muscat Hamburg’grape at mature stage μg · L-1
| 处理 Treatment | 酸类 Acid | 酯类 Ester | 酮类 Ketone | 醛类 Aldehyde | 醇类 Alcohol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照 Control | 24.58 ± 4.39 b | 3.76 ± 2.13 b | 48.53 ± 11.09 a | 595.41 ± 69.00 b | 123.39 ± 19.82 b |
| 轻度胁迫 Light | 21.28 ± 9.10 b | 5.94 ± 3.63 a | 46.70 ± 17.36 a | 1 054.23 ± 215.11 a | 8.74 ± 1.04 c |
| 重度胁迫 Severe | 67.14 ± 16.98 a | 3.16 ± 1.93 b | 24.12 ± 10.60 b | 446.73 ± 45.51 c | 133.06 ± 30.63 a |
| 处理 Treatment | 萜烯类 Terpene | 酚类 Phenolic | 其他类 Others | 总计 Total | |
| 对照 Control | 400.48 ± 43.46 c | 3.18 ± 1.59 b | 13.78 ± 2.84 b | 1 213.11 ± 146.02 b | |
| 轻度胁迫 Light | 442.33 ± 43.07 b | 10.63 ± 4.60 a | 44.75 ± 7.93 a | 1 634.60 ± 277.05 a | |
| 重度胁迫 Severe | 497.98 ± 79.71 a | 2.59 ± 0.92 b | 19.07 ± 7.72 b | 1 193.85 ± 187.22 b |
| 种类 Species | 化合物 Compound | 处理 Treatment | 不同时期相对含量 Relative content | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 55 d | 65 d | 75 d | 85 d | 95 d | |||
| 醛类 Aldehyde | 2-己烯醛 2-Hexenal | 对照Control | 132.84 ± 11.52 a | 137.72 ± 11.98 b | 464.06 ± 63.16 a | 596.72 ± 91.84 a | 509.48 ± 45.00 b |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 132.34 ± 18.47 a | 144.01 ± 27.15 b | 448.62 ± 38.87 a | 580.46 ± 85.53 a | 896.03 ± 135.38 a | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 111.00 ± 9.80 b | 210.02 ± 18.26 a | 429.79 ± 37.86 a | 335.69 ± 29.11 b | 262.26 ± 62.31 c | ||
| 2,4-己二烯醛 (E,E)-2,4- Hexadienal | 对照Control | 22.49 ± 9.17 a | 21.40 ± 2.76 a | 14.29 ± 2.43 a | — | — | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 22.93 ± 2.94 a | 19.01 ± 6.03 a | 19.58 ± 3.65 a | — | 38.73 ± 8.96 a | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 14.01 ± 1.9 a | 24.95 ± 4.34 a | 13.17 ± 3.25 a | — | 38.76 ± 4.13 a | ||
| 苯甲醛 Benzaldehyde | 对照Control | 2.35 ± 1.56 a | 2.04 ± 0.66 a | 3.40 ± 2.06 a | 4.61 ± 1.36 a | 9.00 ± 2.84 b | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 1.80 ± 0.50 a | 2.61 ± 1.82 a | — | 4.16 ± 0.86 a | 11.91 ± 4.09 b | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 3.02 ± 1.01 a | 2.62 ± 1.23 a | 2.54 ± 0.49 a | — | 27.47 ± 12.65 a | ||
| 反式-2-己烯醛 (E)-2-Hexenal | 对照Control | — | 41.93 ± 4.53 a | 11.10 ± 2.38 a | 12.92 ± 3.63 a | 24.51 ± 2.35 b | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 3.03 ± 0.83 | 3.84 ± 1.85 b | 11.49 ± 8.51 a | 12.21 ± 4.45 a | — | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | 5.89 ± 1.70 b | 10.12 ± 5.75 a | — | 43.44 ± 10.07 a | ||
| 2-甲基苯甲醛 2-methyl- Benzaldehyde | 对照Control | 12.91 ± 2.19 b | 20.98 ± 8.63 a | 15.78 ± 4.50 b | — | 34.59 ± 10.50 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 18.99 ± 5.85 ab | 21.08 ± 4.01 a | 22.51 ± 4.77 a | 35.87 ± 6.66 a | — | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 20.34 ± 1.99 a | — | 22.90 ± 4.51 a | 24.50 ± 3.73 a | 49.33 ± 8.86 a | ||
| 酯类 | 丁二酸二乙酯 Butanedioic acid, diethyl ester | 对照Control | 57.59 ± 12.28 a | 6.36 ± 2.44 a | 16.87 ± 2.74 a | — | — |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 23.62 ± 2.87 b | 3.09 ± 0.31 b | 7.69 ± 1.77 b | 1.71 ± 0.29 a | — | ||
| Ester | 重度胁迫Severe | 10.24 ± 2.00 c | 2.68 ± 1.48b | 3.14 ± 1.63 c | 0.85 ± 0.10 b | — | |
| 癸酸乙酯 Decanoic acid, ethyl ester | 对照Control | 5.59 ± 0.61 a | 5.70 ± 0.66 a | 7.84 ± 2.26 a | 6.48 ± 1.04 a | — | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 5.07 ± 1.31 a | 4.34 ± 0.46 a | 7.63 ± 1.80 a | 5.89 ± 1.58 a | — | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 5.11 ± 0.45 a | 4.43 ± 1.41 a | 6.12 ± 3.97 a | 3.79 ± 0.79 a | — | ||
| 水杨酸甲酯 Methyl salicylate | 对照Control | 5.47 ± 1.69 a | 4.18 ± 0.42 a | 3.53 ± 2.67 a | 4.68 ± 1.75 a | 3.76 ± 0.70 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 4.71 ± 1.55 a | 3.62 ± 0.69 a | 4.19 ± 0.55 a | 4.91 ± 1.37 a | 4.80 ± 1.45 a | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 4.09 ± 3.98 a | 4.16 ± 1.09 a | 3.69 ± 1.80 a | 3.07 ± 2.93 a | 3.16 ± 0.45 a | ||
| 邻苯二甲酸 二异丁酯 1,2-Benzene- dicarboxylic acid, bis(2-methylpropyl) ester | 对照Control | — | 0.64 ± 0.25 a | 0.93 ± 0.08 a | 1.88 ± 1.08 a | — | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | 0.71 ± 0.19 a | 1.06 ± 0.74 a | 1.65 ± 0.69 a | — | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 0.72 ± 0.50 | 0.88 ± 0.12 a | 1.11 ± 0.10 a | 0.97 ± 0.82 a | — | ||
Table 5 Effects of water stress on the main aldehydes and esters content of‘Muscat Hamburg’grape during maturity μg · L-1
| 种类 Species | 化合物 Compound | 处理 Treatment | 不同时期相对含量 Relative content | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 55 d | 65 d | 75 d | 85 d | 95 d | |||
| 醛类 Aldehyde | 2-己烯醛 2-Hexenal | 对照Control | 132.84 ± 11.52 a | 137.72 ± 11.98 b | 464.06 ± 63.16 a | 596.72 ± 91.84 a | 509.48 ± 45.00 b |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 132.34 ± 18.47 a | 144.01 ± 27.15 b | 448.62 ± 38.87 a | 580.46 ± 85.53 a | 896.03 ± 135.38 a | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 111.00 ± 9.80 b | 210.02 ± 18.26 a | 429.79 ± 37.86 a | 335.69 ± 29.11 b | 262.26 ± 62.31 c | ||
| 2,4-己二烯醛 (E,E)-2,4- Hexadienal | 对照Control | 22.49 ± 9.17 a | 21.40 ± 2.76 a | 14.29 ± 2.43 a | — | — | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 22.93 ± 2.94 a | 19.01 ± 6.03 a | 19.58 ± 3.65 a | — | 38.73 ± 8.96 a | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 14.01 ± 1.9 a | 24.95 ± 4.34 a | 13.17 ± 3.25 a | — | 38.76 ± 4.13 a | ||
| 苯甲醛 Benzaldehyde | 对照Control | 2.35 ± 1.56 a | 2.04 ± 0.66 a | 3.40 ± 2.06 a | 4.61 ± 1.36 a | 9.00 ± 2.84 b | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 1.80 ± 0.50 a | 2.61 ± 1.82 a | — | 4.16 ± 0.86 a | 11.91 ± 4.09 b | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 3.02 ± 1.01 a | 2.62 ± 1.23 a | 2.54 ± 0.49 a | — | 27.47 ± 12.65 a | ||
| 反式-2-己烯醛 (E)-2-Hexenal | 对照Control | — | 41.93 ± 4.53 a | 11.10 ± 2.38 a | 12.92 ± 3.63 a | 24.51 ± 2.35 b | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 3.03 ± 0.83 | 3.84 ± 1.85 b | 11.49 ± 8.51 a | 12.21 ± 4.45 a | — | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | 5.89 ± 1.70 b | 10.12 ± 5.75 a | — | 43.44 ± 10.07 a | ||
| 2-甲基苯甲醛 2-methyl- Benzaldehyde | 对照Control | 12.91 ± 2.19 b | 20.98 ± 8.63 a | 15.78 ± 4.50 b | — | 34.59 ± 10.50 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 18.99 ± 5.85 ab | 21.08 ± 4.01 a | 22.51 ± 4.77 a | 35.87 ± 6.66 a | — | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 20.34 ± 1.99 a | — | 22.90 ± 4.51 a | 24.50 ± 3.73 a | 49.33 ± 8.86 a | ||
| 酯类 | 丁二酸二乙酯 Butanedioic acid, diethyl ester | 对照Control | 57.59 ± 12.28 a | 6.36 ± 2.44 a | 16.87 ± 2.74 a | — | — |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 23.62 ± 2.87 b | 3.09 ± 0.31 b | 7.69 ± 1.77 b | 1.71 ± 0.29 a | — | ||
| Ester | 重度胁迫Severe | 10.24 ± 2.00 c | 2.68 ± 1.48b | 3.14 ± 1.63 c | 0.85 ± 0.10 b | — | |
| 癸酸乙酯 Decanoic acid, ethyl ester | 对照Control | 5.59 ± 0.61 a | 5.70 ± 0.66 a | 7.84 ± 2.26 a | 6.48 ± 1.04 a | — | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 5.07 ± 1.31 a | 4.34 ± 0.46 a | 7.63 ± 1.80 a | 5.89 ± 1.58 a | — | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 5.11 ± 0.45 a | 4.43 ± 1.41 a | 6.12 ± 3.97 a | 3.79 ± 0.79 a | — | ||
| 水杨酸甲酯 Methyl salicylate | 对照Control | 5.47 ± 1.69 a | 4.18 ± 0.42 a | 3.53 ± 2.67 a | 4.68 ± 1.75 a | 3.76 ± 0.70 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 4.71 ± 1.55 a | 3.62 ± 0.69 a | 4.19 ± 0.55 a | 4.91 ± 1.37 a | 4.80 ± 1.45 a | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 4.09 ± 3.98 a | 4.16 ± 1.09 a | 3.69 ± 1.80 a | 3.07 ± 2.93 a | 3.16 ± 0.45 a | ||
| 邻苯二甲酸 二异丁酯 1,2-Benzene- dicarboxylic acid, bis(2-methylpropyl) ester | 对照Control | — | 0.64 ± 0.25 a | 0.93 ± 0.08 a | 1.88 ± 1.08 a | — | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | 0.71 ± 0.19 a | 1.06 ± 0.74 a | 1.65 ± 0.69 a | — | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 0.72 ± 0.50 | 0.88 ± 0.12 a | 1.11 ± 0.10 a | 0.97 ± 0.82 a | — | ||
| 种类 Species | 化合物 Compound | 处理 Treatment | 不同时期相对含量 Relative content | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 55 d | 65 d | 75 d | 85 d | 95 d | |||
| 醇类 Alcohols | 苯乙醇 Phenylethyl alcohol | 对照Control | 79.37 ± 15.36 a | 23.01 ± 5.64 a | 38.79 ± 6.82 a | 14.56 ± 4.32 a | — |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 40.76 ± 9.85 b | 13.01 ± 1.29 b | 28.22 ± 6.92 a | 12.13 ± 4.32 ab | — | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 24.52 ± 3.79 c | 11.62 ± 1.66 b | 16.06 ± 3.32 a | 7.06 ± 1.10b | — | ||
| 2-乙基己醇 2-ethyl-1-hexanol | 对照Control | 0.89 ± 0.40 a | — | 1.57 ± 1.63 a | 1.21 ± 0.20 a | 2.69 ± 1.50 b | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 0.50 ± 0.37 a | 0.46 ± 0.08 b | 1.49 ± 1.08 a | 1.20 ± 0.20 a | 6.36 ± 2.41b | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 0.70 ± 0.38 a | 0.56 ± 0.11 a | 0.57 ± 0.35 a | 0.66 ± 0.41 a | 21.09 ± 2.48 a | ||
| 3,7-二甲基-1,5,7-辛三烯-3-醇 3,7-dimethyl-2,6-Octadien-1-ol | 对照Control | — | — | 21.45 ± 5.14 ab | 55.14 ± 9.8 a | 109.61 ± 28.09 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | — | 24.90 ± 3.92 a | 57.72 ± 7.39 a | — | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | 1.32 ± 0.27 | 15.79 ± 2.21 b | 26.95 ± 4.65 b | 71.45 ± 30.13 a | ||
| 四氢吡喃-2-甲醇 Tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-methanol | 对照Control | 38.92 ± 8.81 a | 14.10 ± 3.32 b | — | — | — | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 28.81 ± 6.63 ab | 16.55 ± 5.48 ab | — | 1.89 ± 0.80 | — | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 21.21 ± 10.35 a | 25.45 ± 4.31 a | 7.06 ± 1.72 | — | 14.56 ± 3.61 | ||
| 苯甲醇 Benzyl alcohol | 对照Control | — | 1.37 ± 1.37 a | — | — | 1.48 ± 0.91 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | 1.27 ± 0.16 a | — | — | 2.38 ± 0.55 a | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | — | — | — | ||
| 正己醇 1-Hexanol | 对照Control | — | — | 0.50 ± 0.15 | — | 2.45 ± 1.06 | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 0.83 ± 0.54 | 0.75 ± 0.50 | — | 1.05 ± 0.22 | — | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | — | — | — | ||
| 萜烯类 Terpenes | 芳樟醇 Linalool | 对照Control | 15.82 ± 3.85 b | 8.15 ± 0.93 a | 53.53 ± 11.13 a | 148.18 ± 16.04 a | 238.72 ± 56.20 b |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 25.09 ± 5.98 a | 10.80 ± 1.35 a | 49.94 ± 6.93 a | 135.16 ± 17.00 a | 337.79 ± 43.27 ab | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 17.16 ± 4.44 b | 10.70 ± 3.93 a | 38.97 ± 6.42 b | 94.50 ± 13.31b | 434.69 ± 56.31 a | ||
| α-萜品醇 α-Terpineol | 对照Control | 11.51 ± 1.77 a | 8.38 ± 1.30 a | 16.90 ± 2.65 a | 50.93 ± 18.19 a | 86.34 ± 7.65 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 15.06 ± 5.21 a | 9.70 ± 2.29 a | 18.71 ± 3.15 a | 45.70 ± 19.82 a | 54.49 ± 12.51 b | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 15.69 ± 1.98 a | 9.20 ± 1.73 a | 15.69 ± 3.82 a | 30.95 ± 13.92 a | 57.69 ± 6.33 b | ||
| 香叶醇 Geraniol | 对照Control | — | — | 5.71 ± 0.98 a | 11.91 ± 2.19 a | 6.95 ± 2.71 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 6.75 ± 2.27 a | 4.09 ± 1.45 | 5.58 ± 0.78 a | 12.26 ± 3.19 a | 6.84 ± 1.47 a | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 5.85 ± 2.04 a | — | 6.56 ± 1.28 a | 8.98 ± 1.11 a | — | ||
| 顺式氧化芳樟醇 cis-Linaloloxide | 对照Control | — | — | 1.08 ± 0.97 | 2.27 ± 1.03 a | 2.15 ± 0.21 b | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | — | — | 1.99 ± 0.84 a | 2.24 ± 1.08 b | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | — | — | 5.60 ± 1.45 a | ||
| 月桂烯 β-Myrcene | 对照Control | — | — | — | 2.38 ± 0.63 a | 22.68 ± 2.05 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 1.02 ± 0.09 a | — | 4.69 ± 0.76 | 4.10 ± 0.71 a | 11.51 ± 1.91 b | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 0.94 ± 0.27 a | — | — | 2.89 ± 1.55 a | — | ||
| 右旋柠檬烯 D-Limonene | 对照Control | — | — | — | 3.04 ± 2.40 a | 28.77 ± 4.06 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 1.57 ± 0.41 | — | — | — | 17.10 ± 2.74 b | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | — | 1.99 ± 0.90 a | — | ||
Table 6 Effects of water stress on the main alcohols and terpenes content of‘Muscat Hamburg’Grape during maturity μg · L-1
| 种类 Species | 化合物 Compound | 处理 Treatment | 不同时期相对含量 Relative content | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 55 d | 65 d | 75 d | 85 d | 95 d | |||
| 醇类 Alcohols | 苯乙醇 Phenylethyl alcohol | 对照Control | 79.37 ± 15.36 a | 23.01 ± 5.64 a | 38.79 ± 6.82 a | 14.56 ± 4.32 a | — |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 40.76 ± 9.85 b | 13.01 ± 1.29 b | 28.22 ± 6.92 a | 12.13 ± 4.32 ab | — | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 24.52 ± 3.79 c | 11.62 ± 1.66 b | 16.06 ± 3.32 a | 7.06 ± 1.10b | — | ||
| 2-乙基己醇 2-ethyl-1-hexanol | 对照Control | 0.89 ± 0.40 a | — | 1.57 ± 1.63 a | 1.21 ± 0.20 a | 2.69 ± 1.50 b | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 0.50 ± 0.37 a | 0.46 ± 0.08 b | 1.49 ± 1.08 a | 1.20 ± 0.20 a | 6.36 ± 2.41b | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 0.70 ± 0.38 a | 0.56 ± 0.11 a | 0.57 ± 0.35 a | 0.66 ± 0.41 a | 21.09 ± 2.48 a | ||
| 3,7-二甲基-1,5,7-辛三烯-3-醇 3,7-dimethyl-2,6-Octadien-1-ol | 对照Control | — | — | 21.45 ± 5.14 ab | 55.14 ± 9.8 a | 109.61 ± 28.09 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | — | 24.90 ± 3.92 a | 57.72 ± 7.39 a | — | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | 1.32 ± 0.27 | 15.79 ± 2.21 b | 26.95 ± 4.65 b | 71.45 ± 30.13 a | ||
| 四氢吡喃-2-甲醇 Tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-methanol | 对照Control | 38.92 ± 8.81 a | 14.10 ± 3.32 b | — | — | — | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 28.81 ± 6.63 ab | 16.55 ± 5.48 ab | — | 1.89 ± 0.80 | — | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 21.21 ± 10.35 a | 25.45 ± 4.31 a | 7.06 ± 1.72 | — | 14.56 ± 3.61 | ||
| 苯甲醇 Benzyl alcohol | 对照Control | — | 1.37 ± 1.37 a | — | — | 1.48 ± 0.91 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | 1.27 ± 0.16 a | — | — | 2.38 ± 0.55 a | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | — | — | — | ||
| 正己醇 1-Hexanol | 对照Control | — | — | 0.50 ± 0.15 | — | 2.45 ± 1.06 | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 0.83 ± 0.54 | 0.75 ± 0.50 | — | 1.05 ± 0.22 | — | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | — | — | — | ||
| 萜烯类 Terpenes | 芳樟醇 Linalool | 对照Control | 15.82 ± 3.85 b | 8.15 ± 0.93 a | 53.53 ± 11.13 a | 148.18 ± 16.04 a | 238.72 ± 56.20 b |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 25.09 ± 5.98 a | 10.80 ± 1.35 a | 49.94 ± 6.93 a | 135.16 ± 17.00 a | 337.79 ± 43.27 ab | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 17.16 ± 4.44 b | 10.70 ± 3.93 a | 38.97 ± 6.42 b | 94.50 ± 13.31b | 434.69 ± 56.31 a | ||
| α-萜品醇 α-Terpineol | 对照Control | 11.51 ± 1.77 a | 8.38 ± 1.30 a | 16.90 ± 2.65 a | 50.93 ± 18.19 a | 86.34 ± 7.65 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 15.06 ± 5.21 a | 9.70 ± 2.29 a | 18.71 ± 3.15 a | 45.70 ± 19.82 a | 54.49 ± 12.51 b | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 15.69 ± 1.98 a | 9.20 ± 1.73 a | 15.69 ± 3.82 a | 30.95 ± 13.92 a | 57.69 ± 6.33 b | ||
| 香叶醇 Geraniol | 对照Control | — | — | 5.71 ± 0.98 a | 11.91 ± 2.19 a | 6.95 ± 2.71 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 6.75 ± 2.27 a | 4.09 ± 1.45 | 5.58 ± 0.78 a | 12.26 ± 3.19 a | 6.84 ± 1.47 a | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 5.85 ± 2.04 a | — | 6.56 ± 1.28 a | 8.98 ± 1.11 a | — | ||
| 顺式氧化芳樟醇 cis-Linaloloxide | 对照Control | — | — | 1.08 ± 0.97 | 2.27 ± 1.03 a | 2.15 ± 0.21 b | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | — | — | 1.99 ± 0.84 a | 2.24 ± 1.08 b | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | — | — | 5.60 ± 1.45 a | ||
| 月桂烯 β-Myrcene | 对照Control | — | — | — | 2.38 ± 0.63 a | 22.68 ± 2.05 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 1.02 ± 0.09 a | — | 4.69 ± 0.76 | 4.10 ± 0.71 a | 11.51 ± 1.91 b | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 0.94 ± 0.27 a | — | — | 2.89 ± 1.55 a | — | ||
| 右旋柠檬烯 D-Limonene | 对照Control | — | — | — | 3.04 ± 2.40 a | 28.77 ± 4.06 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 1.57 ± 0.41 | — | — | — | 17.10 ± 2.74 b | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | — | 1.99 ± 0.90 a | — | ||
| 种类 Species | 化合物名 Compound name | 处理 Treatment | 不同时期相对含量 Relative content | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 55 d | 65 d | 75 d | 85 d | 95 d | |||
| 酸类 Acids | 乙酸 Acetic acid | 对照Control | 2.80 ± 2.07 a | 1.77 ± 1.17 a | 2.81 ± 1.10 a | 3.05 ± 1.12 a | 11.75 ± 1.66 b |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 2.38 ± 0.37 a | 1.69 ± 0.78 a | 3.05 ± 2.05 a | 3.45 ± 1.46 a | 10.28 ± 0.89 b | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 2.03 ± 0.35 a | 1.88 ± 0.22 a | 2.58 ± 1.51 a | 1.85 ± 1.29 a | 26.76 ± 3.83 a | ||
| 甲酸 Formic acid | 对照Control | 0.47 ± 0.40 a | — | — | — | 2.02 ± 1.56 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 0.54 ± 0.33 a | — | — | — | 1.48 ± 0.68 a | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 0.46 ± 0.15 a | — | — | — | 1.93 ± 1.37 a | ||
| 香叶酸 Geranic acid | 对照Control | 1.84 ± 0.19 b | 2.70 ± 0.25 a | 2.91 ± 0.95 a | 4.35 ± 0.81 a | 1.12 ± 0.88 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 3.76 ± 1.33 a | 2.90 ± 0.37 a | 3.22 ± 1.36 a | 4.39 ± 1.65 a | 1.43 ± 0.25 a | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | 2.51 ± 0.49 a | 3.13 ± 1.63 a | 3.12 ± 1.15 a | — | ||
| 癸酸 n-Decanoic acid | 对照Control | 5.56 ± 1.63 a | 4.23 ± 0.41 a | 4.61 ± 1.58 a | 3.66 ± 1.77 a | — | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 4.54 ± 0.61 a | 2.75 ± 0.90 a | 4.34 ± 1.61 a | 2.99 ± 0.69 a | — | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 3.76 ± 0.88 a | 3.19 ± 1.83 a | 3.51 ± 1.42 a | 2.02 ± 0.18 a | — | ||
| 壬酸 Nonanoic acid | 对照Control | 0.83 ± 0.21 b | 1.41 ± 0.51 a | 1.24 ± 0.20 a | 2.03 ± 1.40 a | 0.56 ± 0.42 | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 1.14 ± 0.10 ab | 1.31 ± 0.51 a | 1.51 ± 0.19 a | 2.06 ± 0.56 a | — | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 1.47 ± 0.34 a | 1.45 ± 0.60 a | 1.59 ± 1.04 a | 1.29 ± 0.30 a | — | ||
| 辛酸 Octanoic acid | 对照Control | 21.55 ± 4.76 a | 4.55 ± 0.58 a | 8.02 ± 4.02 a | 2.23 ± 0.50 a | — | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 10.47 ± 8.95 b | 2.34 ± 0.42 b | 4.62 ± 0.91 a | 1.79 ± 1.88 a | — | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 5.74 ± 1.48 b | 1.87 ± 0.76 b | 2.65 ± 0.97 a | 0.94 ± 0.79 a | — | ||
| 己酸 Hexanoic acid | 对照Control | — | — | — | — | — | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | — | 2.11 ± 0.24 | — | 5.93 ± 3.21 a | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | — | — | 9.57 ± 6.44 a | ||
| 苯甲酸 Benzoic acid | 对照Control | — | — | — | — | 8.07 ± 3.17 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | — | — | — | — | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | — | — | 23.51 ± 16.36 a | ||
| 异辛酸 2-ethyl-Hexanoic acid | 对照Control | — | — | — | — | 1.06 ± 0.34 b | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | — | — | — | 2.16 ± 0.50 b | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | — | — | 5.37 ± 2.41 a | ||
| 酮类 Ketones | 大马酮 Damascone | 对照Control | 8.90 ± 5.34 a | 19.85 ± 7.82 a | 21.49 ± 7.29 a | 33.92 ± 14.39 a | 32.46 ± 18.95 a |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 11.22 ± 4.91 a | 31.30 ± 9.65 a | 31.30 ± 9.65 a | 33.29 ± 5.15 a | 26.62 ± 5.76 a | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 14.56 ± 3.60 a | 24.16 ± 7.76 a | 33.29 ± 4.89 a | 19.38 ± 7.26 a | 13.69 ± 2.65 a | ||
| 2-吡咯烷酮 2-Pyrrolidinone | 对照Control | 1.39 ± 0.19 a | 0.94 ± 0.62 a | 1.32 ± 0.33 a | 1.03 ± 0.45 a | 1.11 ± 0.90 b | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 1.26 ± 0.19 a | 1.29 ± 0.27 a | 1.29 ± 0.19 a | 1.04 ± 0.47 a | 2.02 ± 1.61 b | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 1.14 ± 0.14 a | 0.57 ± 0.08 a | 0.70 ± 0.17 b | 0.71 ± 0.19 a | 4.79 ± 0.83 a | ||
| 1-乙酰-2-吡咯烷酮 N-Acetylpyrrolidone | 对照Control | 2.50 ± 1.35 a | 2.06 ± 1.04 a | 2.60 ± 0.23 a | 3.04 ± 1.71 a | 5.14 ± 0.54 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 2.46 ± 1.70 a | 3.00 ± 1.74 a | 3.00 ± 0.94 a | 2.97 ± 0.82 a | 7.11 ± 1.20 a | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 2.50 ± 0.24 a | 2.00 ± 1.68 a | 1.92 ± 0.77 a | 1.80 ± 0.29 a | — | ||
| 仲辛酮 2-Octanone | 对照Control | — | — | — | — | 2.54 ± 0.86 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 1.87 ± 0.71 a | — | — | — | 3.86 ± 0.98 a | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 1.51 ± 0.13 a | 1.59 ± 0.15 | — | 1.23 ± 0.41 | — | ||
| 4-甲基苯戊酮 1-(4-methylphenyl)-1-Pentanone | 对照Control | — | — | 0.77 ± 0.33 a | 1.75 ± 0.25 a | 2.01 ± 0.37 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | 1.23 ± 0.18 | 1.23 ± 0.42 a | 1.48 ± 0.41 a | 2.12 ± 1.55 a | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | 0.73 ± 0.17 a | 0.67 ± 0.22 b | — | ||
Table 7 Effects of water stress on the main acids and ketones content of‘Muscat Hamburg’grape during maturity μg · L-1
| 种类 Species | 化合物名 Compound name | 处理 Treatment | 不同时期相对含量 Relative content | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 55 d | 65 d | 75 d | 85 d | 95 d | |||
| 酸类 Acids | 乙酸 Acetic acid | 对照Control | 2.80 ± 2.07 a | 1.77 ± 1.17 a | 2.81 ± 1.10 a | 3.05 ± 1.12 a | 11.75 ± 1.66 b |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 2.38 ± 0.37 a | 1.69 ± 0.78 a | 3.05 ± 2.05 a | 3.45 ± 1.46 a | 10.28 ± 0.89 b | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 2.03 ± 0.35 a | 1.88 ± 0.22 a | 2.58 ± 1.51 a | 1.85 ± 1.29 a | 26.76 ± 3.83 a | ||
| 甲酸 Formic acid | 对照Control | 0.47 ± 0.40 a | — | — | — | 2.02 ± 1.56 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 0.54 ± 0.33 a | — | — | — | 1.48 ± 0.68 a | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 0.46 ± 0.15 a | — | — | — | 1.93 ± 1.37 a | ||
| 香叶酸 Geranic acid | 对照Control | 1.84 ± 0.19 b | 2.70 ± 0.25 a | 2.91 ± 0.95 a | 4.35 ± 0.81 a | 1.12 ± 0.88 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 3.76 ± 1.33 a | 2.90 ± 0.37 a | 3.22 ± 1.36 a | 4.39 ± 1.65 a | 1.43 ± 0.25 a | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | 2.51 ± 0.49 a | 3.13 ± 1.63 a | 3.12 ± 1.15 a | — | ||
| 癸酸 n-Decanoic acid | 对照Control | 5.56 ± 1.63 a | 4.23 ± 0.41 a | 4.61 ± 1.58 a | 3.66 ± 1.77 a | — | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 4.54 ± 0.61 a | 2.75 ± 0.90 a | 4.34 ± 1.61 a | 2.99 ± 0.69 a | — | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 3.76 ± 0.88 a | 3.19 ± 1.83 a | 3.51 ± 1.42 a | 2.02 ± 0.18 a | — | ||
| 壬酸 Nonanoic acid | 对照Control | 0.83 ± 0.21 b | 1.41 ± 0.51 a | 1.24 ± 0.20 a | 2.03 ± 1.40 a | 0.56 ± 0.42 | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 1.14 ± 0.10 ab | 1.31 ± 0.51 a | 1.51 ± 0.19 a | 2.06 ± 0.56 a | — | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 1.47 ± 0.34 a | 1.45 ± 0.60 a | 1.59 ± 1.04 a | 1.29 ± 0.30 a | — | ||
| 辛酸 Octanoic acid | 对照Control | 21.55 ± 4.76 a | 4.55 ± 0.58 a | 8.02 ± 4.02 a | 2.23 ± 0.50 a | — | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 10.47 ± 8.95 b | 2.34 ± 0.42 b | 4.62 ± 0.91 a | 1.79 ± 1.88 a | — | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 5.74 ± 1.48 b | 1.87 ± 0.76 b | 2.65 ± 0.97 a | 0.94 ± 0.79 a | — | ||
| 己酸 Hexanoic acid | 对照Control | — | — | — | — | — | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | — | 2.11 ± 0.24 | — | 5.93 ± 3.21 a | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | — | — | 9.57 ± 6.44 a | ||
| 苯甲酸 Benzoic acid | 对照Control | — | — | — | — | 8.07 ± 3.17 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | — | — | — | — | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | — | — | 23.51 ± 16.36 a | ||
| 异辛酸 2-ethyl-Hexanoic acid | 对照Control | — | — | — | — | 1.06 ± 0.34 b | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | — | — | — | 2.16 ± 0.50 b | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | — | — | 5.37 ± 2.41 a | ||
| 酮类 Ketones | 大马酮 Damascone | 对照Control | 8.90 ± 5.34 a | 19.85 ± 7.82 a | 21.49 ± 7.29 a | 33.92 ± 14.39 a | 32.46 ± 18.95 a |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 11.22 ± 4.91 a | 31.30 ± 9.65 a | 31.30 ± 9.65 a | 33.29 ± 5.15 a | 26.62 ± 5.76 a | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 14.56 ± 3.60 a | 24.16 ± 7.76 a | 33.29 ± 4.89 a | 19.38 ± 7.26 a | 13.69 ± 2.65 a | ||
| 2-吡咯烷酮 2-Pyrrolidinone | 对照Control | 1.39 ± 0.19 a | 0.94 ± 0.62 a | 1.32 ± 0.33 a | 1.03 ± 0.45 a | 1.11 ± 0.90 b | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 1.26 ± 0.19 a | 1.29 ± 0.27 a | 1.29 ± 0.19 a | 1.04 ± 0.47 a | 2.02 ± 1.61 b | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 1.14 ± 0.14 a | 0.57 ± 0.08 a | 0.70 ± 0.17 b | 0.71 ± 0.19 a | 4.79 ± 0.83 a | ||
| 1-乙酰-2-吡咯烷酮 N-Acetylpyrrolidone | 对照Control | 2.50 ± 1.35 a | 2.06 ± 1.04 a | 2.60 ± 0.23 a | 3.04 ± 1.71 a | 5.14 ± 0.54 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 2.46 ± 1.70 a | 3.00 ± 1.74 a | 3.00 ± 0.94 a | 2.97 ± 0.82 a | 7.11 ± 1.20 a | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 2.50 ± 0.24 a | 2.00 ± 1.68 a | 1.92 ± 0.77 a | 1.80 ± 0.29 a | — | ||
| 仲辛酮 2-Octanone | 对照Control | — | — | — | — | 2.54 ± 0.86 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | 1.87 ± 0.71 a | — | — | — | 3.86 ± 0.98 a | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 1.51 ± 0.13 a | 1.59 ± 0.15 | — | 1.23 ± 0.41 | — | ||
| 4-甲基苯戊酮 1-(4-methylphenyl)-1-Pentanone | 对照Control | — | — | 0.77 ± 0.33 a | 1.75 ± 0.25 a | 2.01 ± 0.37 a | |
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | 1.23 ± 0.18 | 1.23 ± 0.42 a | 1.48 ± 0.41 a | 2.12 ± 1.55 a | ||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | 0.73 ± 0.17 a | 0.67 ± 0.22 b | — | ||
| 种类 Species | 化合物名称 Compound name | 处理 Treatment | 不同时期相对含量 Relative content | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 55 d | 65 d | 75 d | 85 d | 95 d | ||||||||
| 酚类 Phenols | 2,4-二叔丁基苯酚 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenol | 对照Control | — | 3.02 ± 1.43 a | — | 3.32 ± 1.81 | — | |||||
| 轻度胁迫Light | 2.53 ± 1.06 | 2.56 ± 0.23 a | 3.03 ± 0.49 | — | — | |||||||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||
| 3,5-二叔丁基苯酚 3,5-Di-tert-butylphenol | 对照Control | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 2.82 ± 0.83 | 3.15 ± 0.59 | 3.55 ± 1.82 | — | — | |||||||
| 2-(1,1-二甲基乙基)-6-(1-甲基乙基)苯酚 2-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-6-(1-methylethyl)phenol | 对照Control | — | — | — | — | 3.18 ± 0.62 | ||||||
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||
| 4,6-二叔丁基间苯二酚 4,6-di-tert-Butylresorcinol | 对照Control | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | — | — | — | 9.16 ± 2.55 | |||||||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||
| 3,5-二乙基-苯酚 3,5-diethyl-Phenol | 对照Control | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | — | — | — | 1.47 ± 0.97 | |||||||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||
| 其他 Others | 2,1,3-苯并噻二唑 2,1,3-Benzothiadiazole | 对照Control | 1.14 ± 0.13 a | 2.08 ± 0.22 a | 1.48 ± 0.21 a | 3.35 ± 1.53 a | — | |||||
| 轻度胁迫Light | 1.62 ± 0.93 a | 1.89 ± 0.28 a | — | 3.87 ± 0.72 a | 5.47 ± 1.18 | |||||||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 1.69 ± 0.21 a | 2.34 ± 0.68 a | 2.17 ± 0.38 a | 2.55 ± 0.30 a | — | |||||||
| 戊酸酐 Valeric anhydride | 对照Control | 4.67 ± 2.02 a | 1.95 ± 0.33 a | — | 1.96 ± 0.17 | — | ||||||
| 轻度胁迫Light | 4.19 ± 1.46 a | 2.21 ± 0.90 a | 2.06 ± 0.64 a | — | — | |||||||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 2.71 ± 0.93 a | 3.11 ± 0.49 a | 0.73 ± 0.32 b | — | — | |||||||
| 对苯二甲醚 1,4-dimethoxy-Benzene | 对照Control | — | 2.39 ± 0.72 a | 2.35 ± 0.38 a | 4.81 ± 0.73 a | 4.25 ± 0.44 a | ||||||
| 轻度胁迫Light | 2.26 ± 1.34 | 2.35 ± 1.37 a | 3.05 ± 0.71 a | 5.18 ± 1.44 a | — | |||||||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | 2.89 ± 0.31 a | 3.14 ± 1.43 a | 3.35 ± 1.08 a | 3.97 ± 1.24 a | |||||||
| 丙基-环丙烷 Propyl-Cyclopropane | 对照Control | — | — | — | 0.73 ± 0.44 a | — | ||||||
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | — | 0.81 ± 0.37 a | — | 4.04 ± 1.32 a | |||||||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 0.52 ± 0.06 | — | 0.61 ± 0.29 a | 0.50 ± 0.11 a | 5.49 ± 1.14 a | |||||||
| 丁醛肟 Oxime butanal | 对照Control | — | — | 1.46 ± 0.15 b | 2.08 ± 0.76 a | — | ||||||
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | — | 1.51 ± 0.18 b | 2.38 ± 0.62 a | — | |||||||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | 1.64 ± 0.14 a | 1.20 ± 0.37 a | 3.59 ± 0.88 | |||||||
Table 8 Effects of water stress on the main phenols and others content of‘Muscat Hamburg’grape during maturity μg · L-1
| 种类 Species | 化合物名称 Compound name | 处理 Treatment | 不同时期相对含量 Relative content | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 55 d | 65 d | 75 d | 85 d | 95 d | ||||||||
| 酚类 Phenols | 2,4-二叔丁基苯酚 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenol | 对照Control | — | 3.02 ± 1.43 a | — | 3.32 ± 1.81 | — | |||||
| 轻度胁迫Light | 2.53 ± 1.06 | 2.56 ± 0.23 a | 3.03 ± 0.49 | — | — | |||||||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||
| 3,5-二叔丁基苯酚 3,5-Di-tert-butylphenol | 对照Control | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 2.82 ± 0.83 | 3.15 ± 0.59 | 3.55 ± 1.82 | — | — | |||||||
| 2-(1,1-二甲基乙基)-6-(1-甲基乙基)苯酚 2-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-6-(1-methylethyl)phenol | 对照Control | — | — | — | — | 3.18 ± 0.62 | ||||||
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||
| 4,6-二叔丁基间苯二酚 4,6-di-tert-Butylresorcinol | 对照Control | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | — | — | — | 9.16 ± 2.55 | |||||||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||
| 3,5-二乙基-苯酚 3,5-diethyl-Phenol | 对照Control | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | — | — | — | 1.47 ± 0.97 | |||||||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||
| 其他 Others | 2,1,3-苯并噻二唑 2,1,3-Benzothiadiazole | 对照Control | 1.14 ± 0.13 a | 2.08 ± 0.22 a | 1.48 ± 0.21 a | 3.35 ± 1.53 a | — | |||||
| 轻度胁迫Light | 1.62 ± 0.93 a | 1.89 ± 0.28 a | — | 3.87 ± 0.72 a | 5.47 ± 1.18 | |||||||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 1.69 ± 0.21 a | 2.34 ± 0.68 a | 2.17 ± 0.38 a | 2.55 ± 0.30 a | — | |||||||
| 戊酸酐 Valeric anhydride | 对照Control | 4.67 ± 2.02 a | 1.95 ± 0.33 a | — | 1.96 ± 0.17 | — | ||||||
| 轻度胁迫Light | 4.19 ± 1.46 a | 2.21 ± 0.90 a | 2.06 ± 0.64 a | — | — | |||||||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 2.71 ± 0.93 a | 3.11 ± 0.49 a | 0.73 ± 0.32 b | — | — | |||||||
| 对苯二甲醚 1,4-dimethoxy-Benzene | 对照Control | — | 2.39 ± 0.72 a | 2.35 ± 0.38 a | 4.81 ± 0.73 a | 4.25 ± 0.44 a | ||||||
| 轻度胁迫Light | 2.26 ± 1.34 | 2.35 ± 1.37 a | 3.05 ± 0.71 a | 5.18 ± 1.44 a | — | |||||||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | 2.89 ± 0.31 a | 3.14 ± 1.43 a | 3.35 ± 1.08 a | 3.97 ± 1.24 a | |||||||
| 丙基-环丙烷 Propyl-Cyclopropane | 对照Control | — | — | — | 0.73 ± 0.44 a | — | ||||||
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | — | 0.81 ± 0.37 a | — | 4.04 ± 1.32 a | |||||||
| 重度胁迫Severe | 0.52 ± 0.06 | — | 0.61 ± 0.29 a | 0.50 ± 0.11 a | 5.49 ± 1.14 a | |||||||
| 丁醛肟 Oxime butanal | 对照Control | — | — | 1.46 ± 0.15 b | 2.08 ± 0.76 a | — | ||||||
| 轻度胁迫Light | — | — | 1.51 ± 0.18 b | 2.38 ± 0.62 a | — | |||||||
| 重度胁迫Severe | — | — | 1.64 ± 0.14 a | 1.20 ± 0.37 a | 3.59 ± 0.88 | |||||||
| [1] |
Acevedo-opazo C, Ortega-farias S, Fuentes S. 2010. Effects of grapevine(Vitis vinifera L.)water status on water consumption,vegetative growth and grape quality:an irrigation scheduling application to achieve regulated deficit irrigation. Agricultural Water Management, 97(7):956-964.
doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2010.01.025 URL |
| [2] |
Bindon K A, Dry P R, Loveys B R. 2007. Influence of plant water status on the production of C13-norisoprenoid precursors in Vitis vinifera L. cv. Cabernet Sauvignon grape berries. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 55(11):4493-4500.
doi: 10.1021/jf063331p URL |
| [3] |
Bonghi C, Rizzini F M, Gambuti A, Moio L, Chkaiban L, Tonutti P. 2012. Phenol compound metabolism and gene expression in the skin of wine grape(Vitis vinifera L.)berries subjected to partial postharvest dehydration. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 67:102-109.
doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2012.01.002 URL |
| [4] |
Brillante L, Martínez-lüscher J, Kurtural S K. 2018. Applied water and mechanical canopy management affect berry and wine phenolic and aroma composition of grapevine(Vitis vinifera L. cv. Syrah)in Central California. Scientia Horticulturae, 227:261-271.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2017.09.048 URL |
| [5] |
Chaves M M, Santos T P, Souza C R, Ortuño M F, Rodrigues M L, Lopes C M, Maroco J P, Pereira J S. 2007. Deficit irrigation in grapevine improves water-use efficiency while controlling vigour and production quality. Annals of Applied Biology, 150(2):237-252.
doi: 10.1111/aab.2007.150.issue-2 URL |
| [6] |
Cooper C M, Davies N W, Menary R C. 2009. Changes in some carotenoids and apocarotenoids during flower development in Boronia megastigma(Nees). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 57(4):1513-1520.
doi: 10.1021/jf802610p URL |
| [7] |
Degenhardt J, Köllner T G, Gershenzon J. 2009. Monoterpene and sesquiterpene synthases and the origin of terpene skeletal diversity in plants. Phytochemistry, 70(15-16):1621-1637.
doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2009.07.030 pmid: 19793600 |
| [8] |
D'onofrio C, Matarese F, Cuzzola A. 2018. Effect of methyl jasmonate on the aroma of Sangiovese grapes and wines. Food Chemistry, 242:352-361.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.09.084 URL |
| [9] |
Edwards E J, Clingeleffer P R. 2013. Interseasonal effects of regulated deficit irrigation on growth,yield,water use,berry composition and wine attributes of Cabernet Sauvignon grapevines. Australian Journal of Grape and Wine Research, 19(2):261-276.
doi: 10.1111/ajgw.12027 URL |
| [10] |
Fenoll J, Manso A, Hellin P, Ruiz L, Flores P. 2009. Changes in the aromatic composition of the Vitis vinifera grape Muscat Hamburg during ripening. Food Chemistry, 114(2):420-428.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.09.060 URL |
| [11] | Fraga H, Malheiro A C, Moutinho P J, Santos J A. 2013. Future scenarios for viticultural zoning in Europe:ensemble projections and uncertainties. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 57(6):909-925. |
| [12] | Hu Hong-yuan, Wang Zhen-ping. 2017. Effects of drought stress on leaf water content and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of Cabernet Sauvignon. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 31(4):124-130. (in Chinese) |
| 胡宏远, 王振平. 2017. 干旱胁迫对赤霞珠葡萄叶片水分及叶绿素荧光参数的影响. 干旱区资源与环境, 31(4):124-130. | |
| [13] |
Leeuwen C, Darriet P. 2016. The impact of climate change on viticulture and wine quality. Journal of Wine Economics, 11(1):150-167.
doi: 10.1017/jwe.2015.21 URL |
| [14] |
Liu G T, Chai F M, Wang Y, Jiang J Z, Duan W, Wang Y T, Wang F F, Li S H, Wang L J. 2018. Genome-wide identification and classification of HSF family in grape,and their transcriptional analysis under heat acclimation and heat stress. Horticultural Plant Journal, 4(4):133-143.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2018.06.001 URL |
| [15] | Lou Yu-sui, Wang Shi-ping, Miao Yu-bin, Lü Zhong-wei, Wang Peng, Xu Guang-min. 2018. Effect of different irrigation thresholds on tree growth and fruit quality in‘Kyoho’grape. Journal of Fruit Science, 35(1):46-55. (in Chinese) |
| 娄玉穗, 王世平, 苗玉彬, 吕中伟, 王鹏, 许广敏. 2018. 不同灌溉阈值对‘巨峰’葡萄树体生长与果实品质的影响. 果树学报, 35(1):46-55. | |
| [16] |
Luan F, Wüst M. 2002. Differential incorporation of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose into (3S)-linalool and geraniol in grape berry exocarp and mesocarp. Phytochemistry, 60(5):451-459.
doi: 10.1016/S0031-9422(02)00147-4 URL |
| [17] |
Mathieu S, Terrier N, Procureur J, Bigey F, Günata Z. 2005. A carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase from Vitis vinifera L.:functional characterization and expression during grape berry development in relation to C13-norisoprenoid accumulation. Journal of Experimental Botany, 56(420):2721-2731.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/eri265 URL |
| [18] |
Niculcea M, López J, Sánchez-díaz M and Carmen A M. 2014. Involvement of berry hormonal content in the response to pre-and post-veraison water deficit in different grapevine(Vitis vinifera L.)cultivars. Australian Journal of Grape and Wine Research, 20:281-291.
doi: 10.1111/ajgw.2014.20.issue-2 URL |
| [19] | Niu Zao-zhu, Chen Zhan, Zhao Yan-zhuo, Niu Shuai-ke, Wei Jian-guo, Yang Li-li. 2019. Analysis of aromatic components from the berries of fifteen grape varieties by GC-MS. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 34(S1):85-91. |
| 牛早柱, 陈展, 赵艳卓, 牛帅科, 魏建国, 杨丽丽. 2019. 15个不同葡萄品种果实香气成分的GC-MS分析. 华北农学报, 34(S1):85-91. | |
| [20] | Pastenes C, Villalobos L, Ríos N, Reyesa F, Turgeonb R, Franck N. 2014. Carbon partitioning to berries in water stressed grapevines;the role of active transport in leaves and fruits. Environmental & Experimental Botany, 107:154-166. |
| [21] |
Santesteban L G, Miranda C, Royo J B. 2011. Regulated deficit irrigation effects on growth,yield,grape quality and individual anthocyanin composition in Vitis vinifera L. cv.‘Tempranillo’. Agricultural Water Management, 98(7):1171-1179.
doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2011.02.011 URL |
| [22] | Sun L, Zhu B Q, Sun X R, Xu X Q, Zhang G J, Yan A L, Xu H Y. 2015. Monoterpene accumulation and its biosynthesis:gene transcript profiles of two grape cultivars during berry development. Acta Horticulturae, 1082:37-42. |
| [23] | Tao Yong-sheng, Liu Ji-bin, Lan Yuan-yuan, Chen Chao-qi, Li Ai-hua. 2016. Instrumental and sensory aroma analysis of noble-rot wine from artificial botrytized grapes. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 47(2):270-279,315. (in Chinese) |
| 陶永胜, 刘吉彬, 兰圆圆, 陈超奇, 李爱华. 2016. 人工贵腐葡萄酒香气的仪器分析与感官评价. 农业机械学报, 47(2):270-279,315. | |
| [24] | Wang Hui-ling, Wang Xiao-yue, Yan Ai-ling, Sun Lei, Zhang Guo-jun, Ren Jian-cheng, Xu Hai-ying. 2019. The accumulation of monoterpenes and the expression of its biosynthesis related genes in‘Aishen Meigui’grape berries cultivated in different trellis systems during ripening stage. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 52(7):1136-1149. (in Chinese) |
| 王慧玲, 王晓玥, 闫爱玲, 孙磊, 张国军, 任建成, 徐海英. 2019. 不同架式‘爱神玫瑰’葡萄果实成熟期间单萜积累及相关基因的表达. 中国农业科学, 52(7):1136-1149. | |
| [25] | Wang J F, Abbey T, Kozak B, Madilao L L, Tindjau R, Nin D J, Castellarin S D. 2019. Evolution over the growing season of volatile organic compounds in Viognier(Vitis vinifera L.)grapes under three irrigation regimes. Food Research International, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2019.108512. |
| [26] | Wang Ji-yuan, Feng Jiao, Hou Xu-dong, Tao Jian-min. 2016. Effects of CPPU on aroma components and biosynthetic genes expression in‘Shine Muscat’grapes. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 39(6):915-923. (in Chinese) |
| 王继源, 冯娇, 侯旭东, 陶建敏. 2016. CPPU对‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄品质及香气合成相关基因表达的影响. 南京农业大学学报, 39(6):915-923. | |
| [27] | Wang Sheng-hai, Yang Wei-wei, Rong Xin-min, Chang Fei-yan, Zhu Jing-jing, Zhang Xiao-yun, Liu Huai-feng. 2019. Effects of training system and water stress on the photosynthetic characteristics of Zixiang Seedless grape leaves based on photosynthetic models. Journal of Shihezi University(Natural Science), 37(4):452-459. (in Chinese) |
| 王生海, 杨伟伟, 容新民, 常飞燕, 朱敬敬, 张晓云, 刘怀锋. 2019. 整形和水分胁迫对紫香无核葡萄叶片光合特性的影响. 石河子大学学报(自然科学版), 37(4):452-459. | |
| [28] | Wang Zhi-qun, Duan Chang-qing, Zhu Bao-qing, Wu Yu-wen, Tu Cui, Pan Qiu-hong. 2011. Relationship between(-)-α-terpineol accumulation and Vvter expression in grape berries . Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 38(11):2187-2192. |
| 王志群, 段长青, 朱保庆, 吴玉文, 涂崔, 潘秋红. 2011. 葡萄果实中(-)-α-萜品醇的积累与其合成酶基因Vvter表达的关系. 园艺学报, 38(11):2187-2192. | |
| [29] | Wen Y Q, Zhong G Y, Gao Y, Lan Y B, Duan C Q, Pan Q H. 2015. Using the combined analysis of transcripts and metabolites to propose key genes for differential terpene accumulation across two regions. BMC Plant Biology, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-015-0631-1. |
| [30] | Wen Ya-qin. 2015. Accumulation of free and glycosidically-bound terpenes and its transcriptional regulation in wine grapes[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Beijing:China Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 问亚琴. 2015. 酿酒葡萄果实游离态和糖苷结合态萜烯的积累及其转录调控[博士论文]. 北京:中国农业大学. | |
| [31] | Xi Ben, Liu Qiao-zhen, Lü Dan-gui, Xu Wei-rong, Wang Zhen-ping, Dai Hong-jun. 2019. Effects of water stress on expression of genes related to resveratrol biosynthesis in grape berries. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 33(8):1490-1500. (in Chinese) |
| 席奔, 柳巧禛, 吕丹桂, 徐伟荣, 王振平, 代红军. 2019. 水分胁迫对葡萄果实白藜芦醇合成相关基因表达的影响. 核农学报, 33(8):1490-1500. | |
| [32] | Yang Chang-yu, Zhang Rui, Lin Bao-jun, Wang Teng-fei, Wang Chun-hong. 2020. Review of effects of water stress on fruit quality of table grapes. Agricultural Engineering, 10(1):86-91. (in Chinese) |
| 杨昌钰, 张芮, 蔺宝军, 王腾飞, 王春宏. 2020. 水分胁迫对鲜食葡萄果实品质影响的研究进展. 农业工程, 10(1):86-91. | |
| [33] |
Yuan J H, Dai Z W, Zhao J Y, Li S H. 2009. Distribution of newly fixed 14C-photoassimilate under deficit irrigation and half-root stress in peach trees. Plant Science, 177(6):691-697.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2009.09.006 URL |
| [34] | Yue Yuan, Liu Jing, Zhang Cun-zhi. 2018. Optimization of extraction conditions of volatile compounds from Muscat by HS-SPME-GC-MS. China Brewing, 37(10):171-176. (in Chinese) |
| 岳圆, 刘晶, 张存智. 2018. HS-SPME-GC-MS分析玫瑰香葡萄中挥发性物质的萃取条件优化. 中国酿造, 37(10):171-176. | |
| [35] | Zhang Q Y, Feng C, Li W H, Qu Z H, Zeng M, Xi W P. 2019. Transcriptional regulatory networks controlling taste and aroma quality of apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.)fruit during ripening. BioMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-5424-8. |
| [36] | Zhou Xiao-fang, Zhang Fu-qing, Liu Jian-fu, Zhang Jun, Lü Wen, Yu Ran. 2014. Progress in research of cultivation technique of the Muscat Hamburg grape in China. Tianjin Agricultural Sciences, 20(6):97-102. (in Chinese) |
| 周晓芳, 张福庆, 刘建福, 张军, 吕文, 俞然. 2014. 我国玫瑰香葡萄品种栽培技术研究进展. 天津农业科学, 20(6):97-102. | |
| [37] |
Zhu B Q, Cai J, Wang Z Q, Xu X Q, Duan C Q, Pan Q H. 2014. Identification of a plastid-localized bifunctional nerolidol/linalool synthase in relation to linalool biosynthesis in young grape berries. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(12):21992-22010.
doi: 10.3390/ijms151221992 URL |
| [1] | WANG Xiaochen, NIE Ziye, LIU Xianju, DUAN Wei, FAN Peige, and LIANG Zhenchang, . Effects of Abscisic Acid on Monoterpene Synthesis in‘Jingxiangyu’Grape Berries [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 237-249. |
| [2] | ZHAI Hanhan, ZHAI Yujie, TIAN Yi, ZHANG Ye, YANG Li, WEN Zhiliang, CHEN Haijiang. Genome-wide Identification of Peach SAUR Gene Family and Characterization of PpSAUR5 Gene [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 1-14. |
| [3] | WANG Baoliang, LIU Fengzhi, JI Xiaohao, WANG Xiaodi, SHI Xiangbin, ZHANG Yican, LI Peng, and WANG Haibo. A New Early Ripening Grape Cultivar‘Huapu Zaoyu’for Table [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 33-34. |
| [4] | WANG Baoliang, WANG Haibo, JI Xiaohao, WANG Xiaodi, SHI Xiangbin, WANG Zhiqiang, WANG Xiaolong, and LIU Fengzhi. A New Middle Ripening Grape Cultivar‘Huapu Huangyu’for Table [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 35-36. |
| [5] | A Late-maturing Seedless Grape Cultivar‘Zilongzhu’. A Late-maturing Seedless Grape Cultivar‘Zilongzhu’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 37-38. |
| [6] | SHI Xiaoxin, DU Guoqiang, YANG Lili, QIAO Yuelian, HUANG Chengli, WANG Suyue, ZHAO Yuexin, WEI Xiaohui, WANG Li, and QI Xiangli. A Late-ripening Seedless Grape Cultivar‘Hongfeng Wuhe’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 39-40. |
| [7] | WU Yueyan, CHEN Tianchi, WANG Liru, HAN Shanqi, and FU Tao. A New Table Grape Cultivar‘Yongzaohong’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 41-42. |
| [8] | WANG Xiaoyue, YAN Ailing, ZHANG Guojun, WANG Huiling, REN Jiancheng, LIU Zhenhua, SUN Lei, and XU Haiying, . A New Grape Cultivar‘Ruidu Wanhong’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 29-30. |
| [9] | WANG Yongjian, KONG Junhua, FAN Peige, LIANG Zhenchang, JIN Xiuliang, LIU Buchun, DAI Zhanwu. Grape Phenome High-throughput Acquisition and Analysis Methods:A Review [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1815-1832. |
| [10] | ZHANG Qiuyue, LIU Changlai, YU Xiaojing, YANG Jiading, FENG Chaonian. Screening of Reference Genes for Differentially Expressed Genes in Pyrus betulaefolia Plant Under Salt Stress by qRT-PCR [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1557-1570. |
| [11] | WEI Xiaoyu, WANG Yuejin. Correlation Between Anatomical Structure and Resistance to Powdery Mildew in Chinese Wild Vitis Species [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1200-1212. |
| [12] | LIU Zhongjie, ZHENG Ting, ZHAO Fanggui, FU Weihong, ZHUGE Yaxian, ZHANG Zhichang, FANG Jinggui. Resistance Difference and Physiological Response Mechanism of Grape Rootstocks to Osmotic Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 984-994. |
| [13] | LIANG Chen, SUN Ruyi, XIANG Rui, SUN Yimeng, SHI Xiaoxin, DU Guoqiang, WANG Li. Genome-wide Identification of Grape GRF Family and Expression Analysis [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 995-1007. |
| [14] | LI Shasha, YU Saisai, FU Yuheng, LUO Qiangwei, XU Yan, WANG Yuejin. The Embryo Rescue and Molecular Markers are Used to Breed New Seedless,Cold-Resistant Grapes [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(4): 723-738. |
| [15] | LI Yamei, MA Fuli, ZHANG Shanqi, HUANG Jinqiu, CHEN Mengting, ZHOU Junyong, SUN Qibao, SUN Jun. Optimization of Jujube Callus Transformation System and Application of ZjBRC1 in Regulating ZjYUCCA Expression [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(4): 749-757. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd